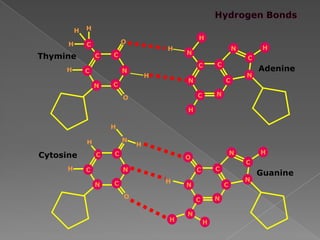
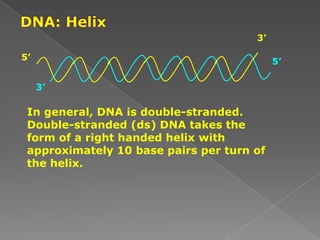
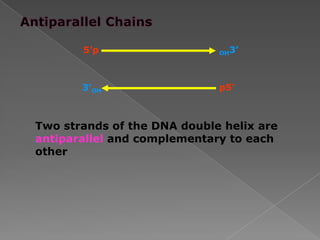
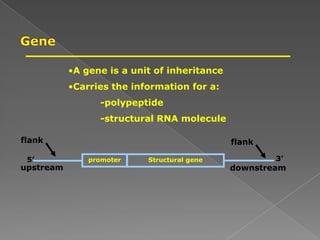
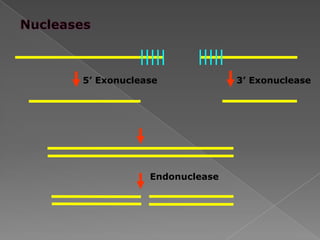
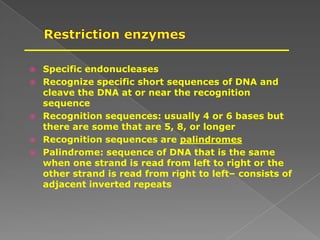
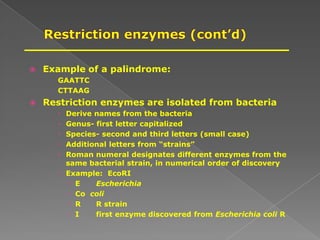
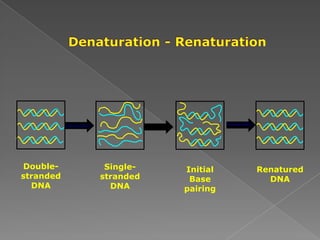
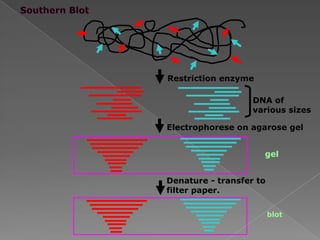
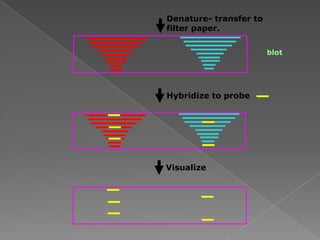
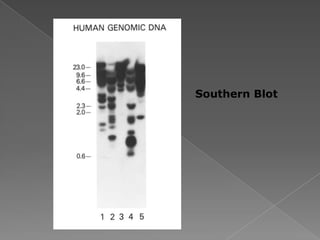
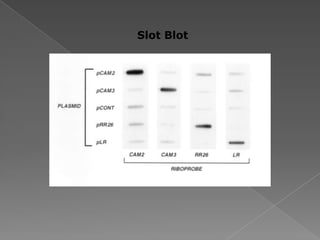
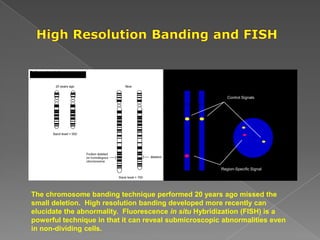
DNA is the genetic material found in chromosomes inside cells. It contains the biological instructions that determine traits like eye color. DNA is made of nucleotides with a phosphate group, sugar (deoxyribose), and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine. DNA exists as two strands coiled around each other in the famous double helix structure, with the bases on one strand pairing with their complements on the other strand. Molecular techniques use DNA, RNA, and enzymes to study biology at a molecular level and detect disease states.