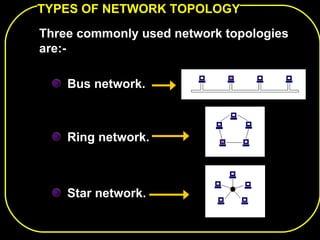
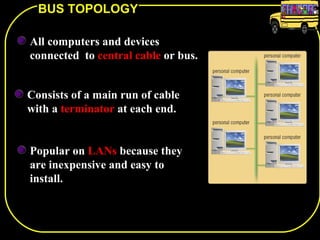
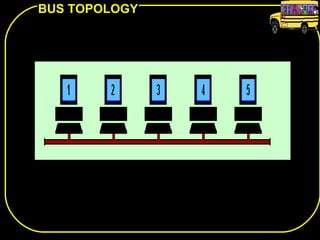
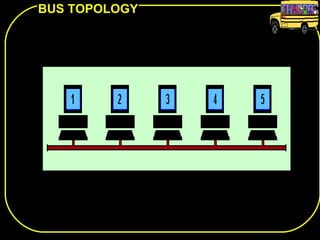
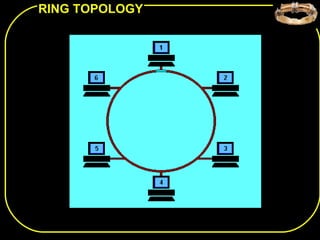
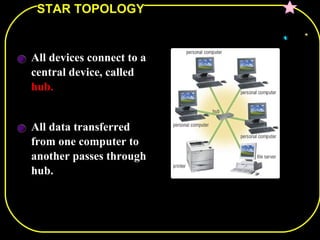
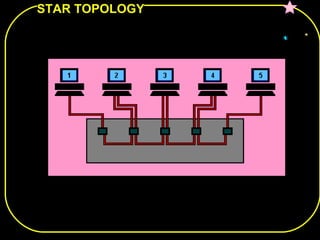
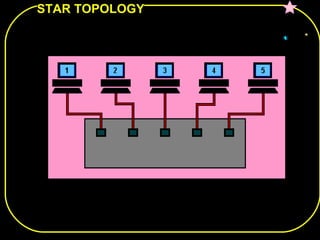
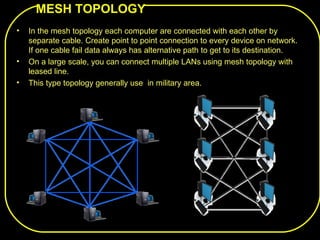
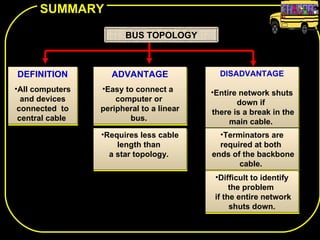
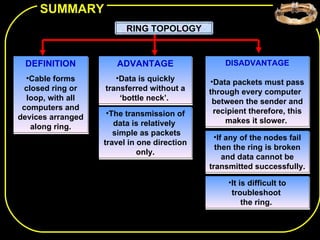
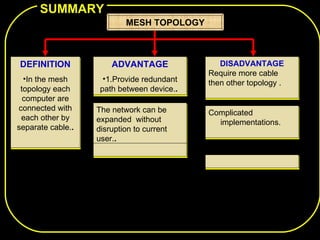
The document discusses different network topologies including bus, ring, star, and mesh. A bus topology connects all devices to a central cable or bus. A ring topology uses a closed cable ring with devices arranged along it and data traveling in one direction. A star topology connects all devices to a central hub with data passing through the hub. A mesh topology connects each device to every other device via separate cables, providing redundant paths. Advantages and disadvantages of each are described.