This document provides background information on modern China, including:
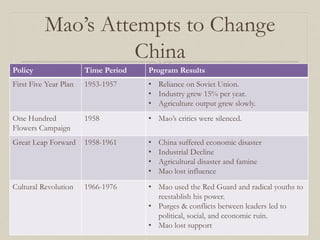
- Mao Zedong's rule and failed economic programs like the Great Leap Forward, which caused famine and economic disaster.
- After Mao's death, Deng Xiaoping rose to power and implemented economic reforms like the Four Modernizations to transform China into an economic power through market-oriented reforms.
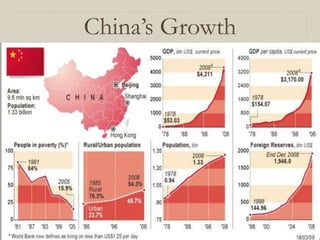
- China experienced rapid economic growth under Deng's policies, but political reforms stalled as the Tiananmen Square protests in 1989 were crushed by the government.
- Today, China is a rising global economic power but maintains a single-party authoritarian political system with restrictions on civil and political liberties.