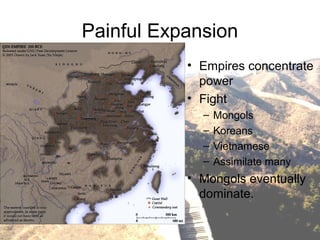
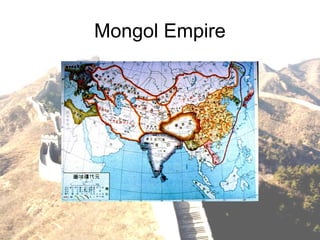
This document provides a historical overview of China from early dynasties to modern times. It discusses the development of Chinese philosophy and empires expanding through fighting neighbors. The Mongols eventually dominated before the Qing Dynasty rose to power in 1644. European powers interfered and forced trade, leading to the Opium Wars. Communism emerged in the 20th century under Mao Zedong, whose Great Leap Forward policy led to millions starving. Economic reforms since 1978 have spurred rapid growth, though corruption and environmental issues persist. Trade with the US has increased but political and military tensions remain over Taiwan and military spending.