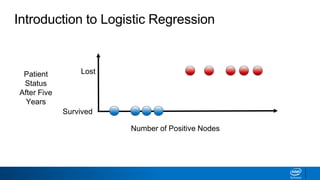
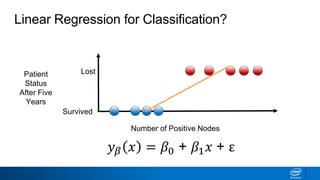
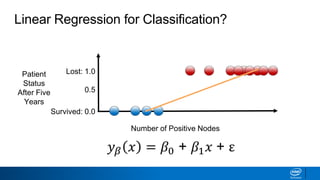
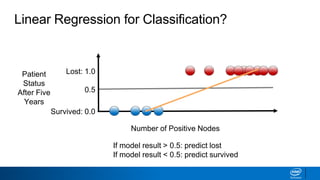
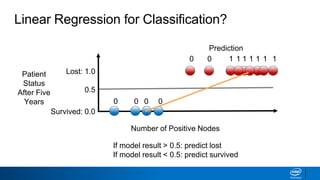
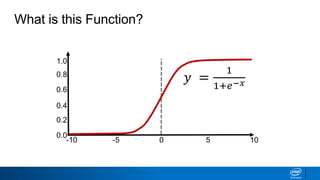
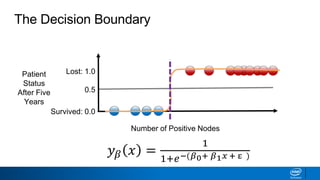
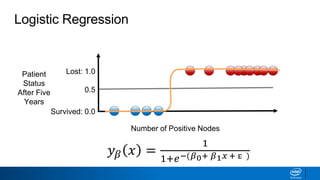
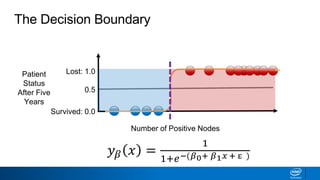
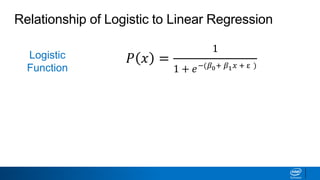
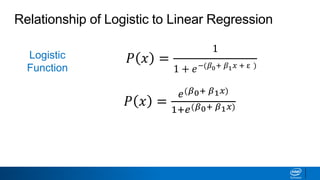
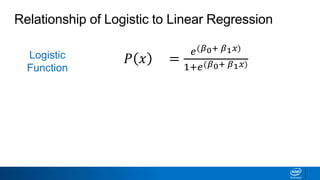
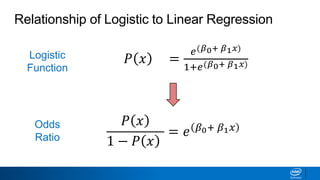
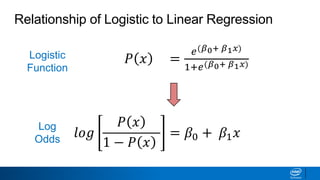
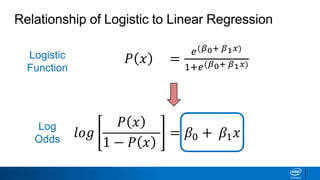
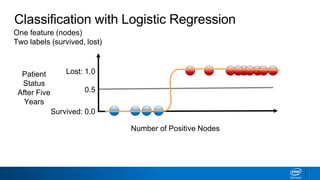
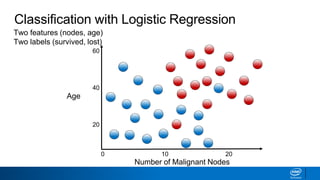
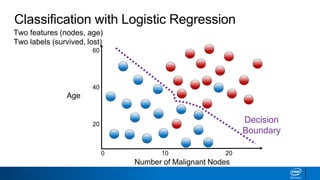
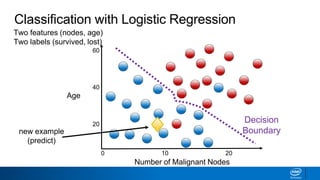
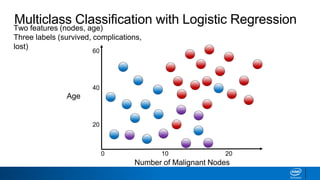
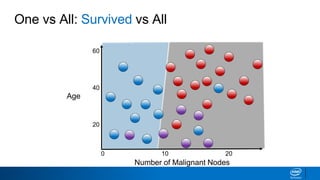
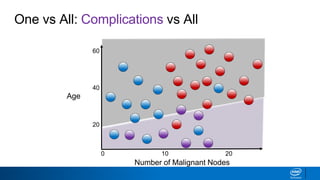
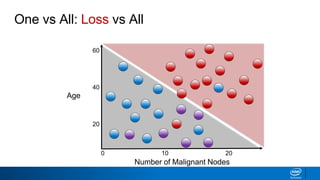
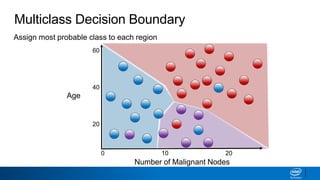
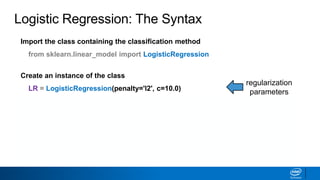
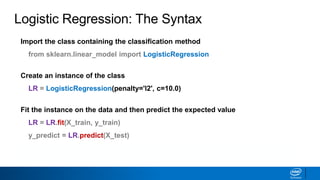
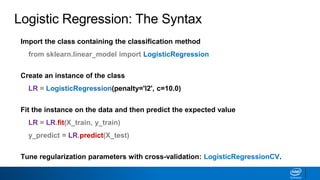
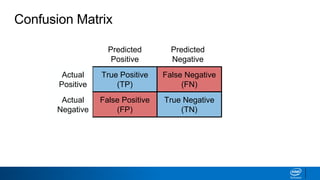
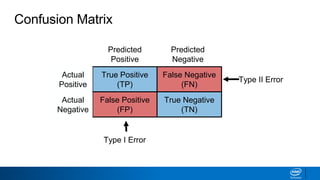
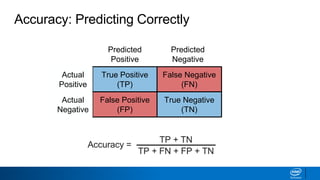
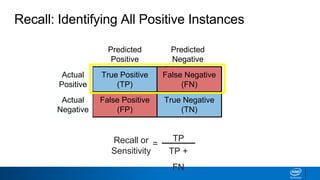
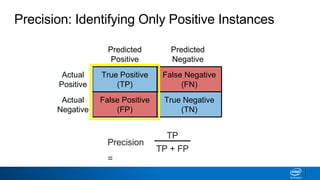
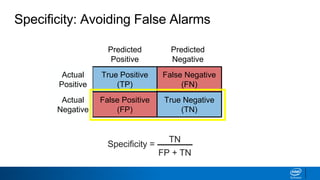
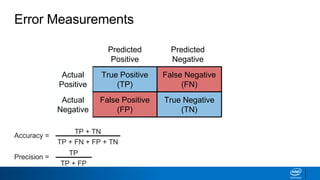
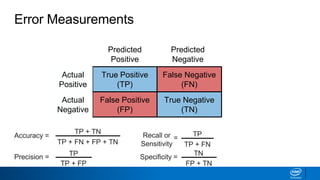
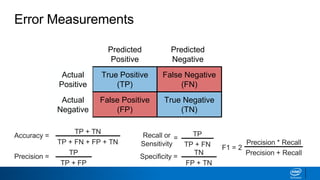
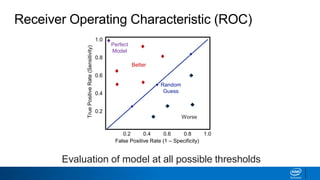
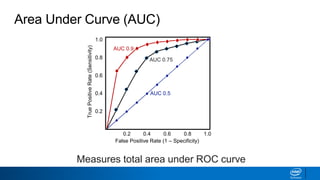
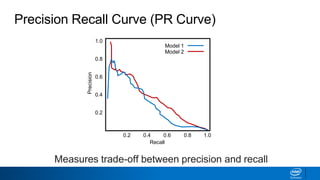
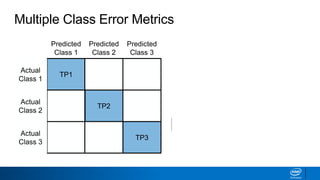
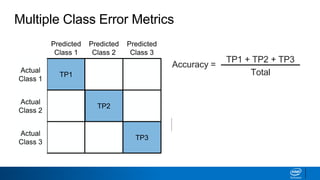
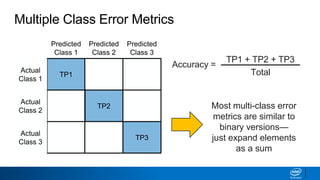
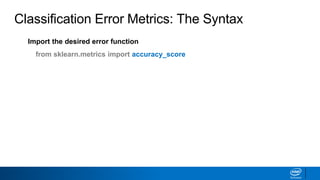
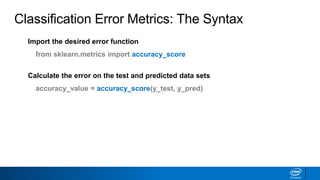
This document provides an introduction to logistic regression. It begins by explaining how linear regression is not suitable for classification problems and introduces the logistic function which maps linear regression output between 0 and 1. This probability value can then be used for classification by setting a threshold of 0.5. The logistic function models the odds ratio as a linear function, allowing logistic regression to be used for binary classification. It can also be extended to multiclass classification problems. The document demonstrates how logistic regression finds a decision boundary to separate classes and how its syntax works in scikit-learn using common error metrics to evaluate performance.