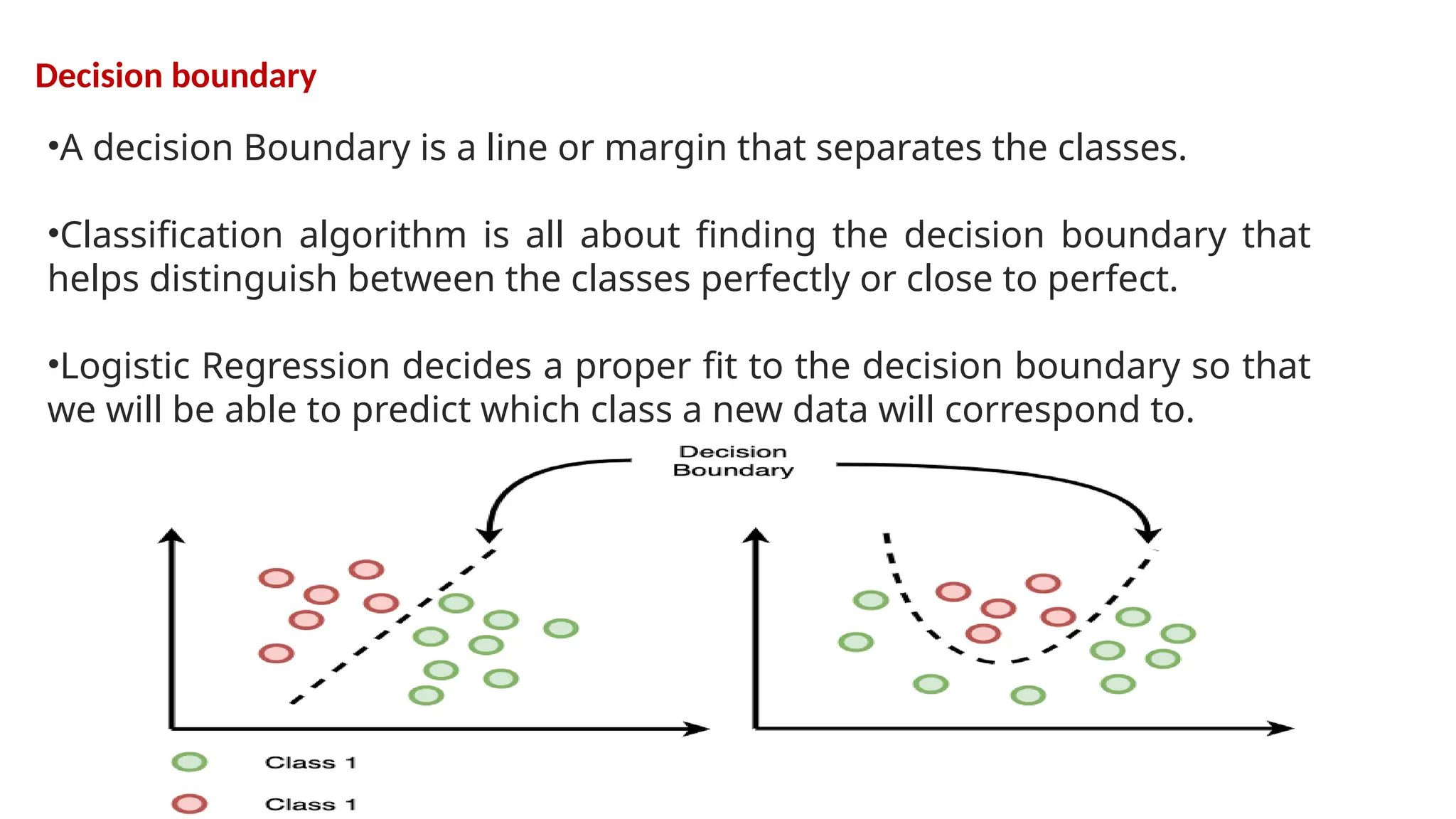
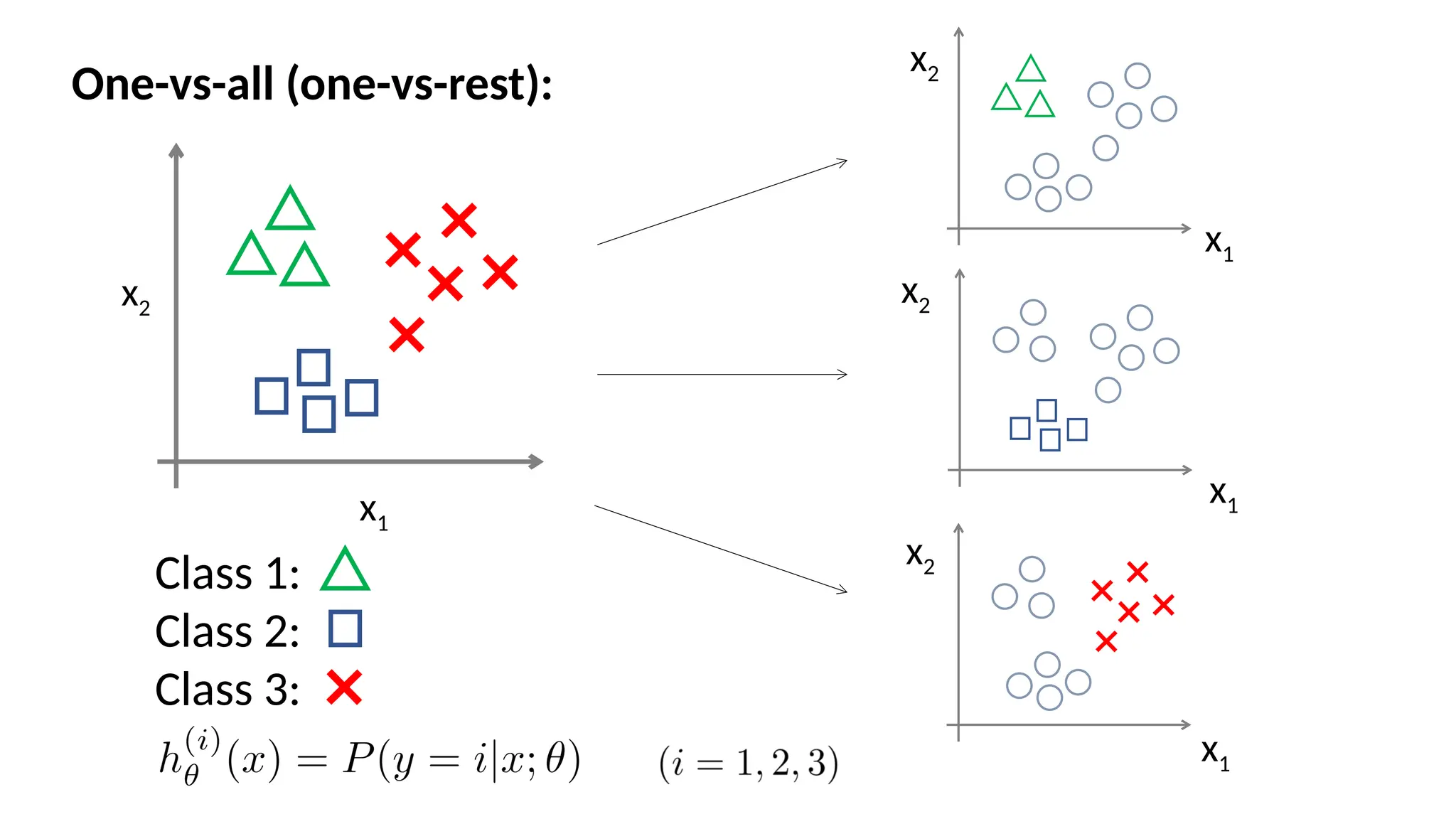
Logistic regression is a supervised statistical technique used primarily for binary classification problems, estimating the probability of a dependent variable and utilizing logit and sigmoid functions to derive relationships between variables. It distinguishes classes by finding decision boundaries and is often preferred for its simplicity and interpretability, although it is limited in handling categorical features and may suffer from overfitting. The cost function in logistic regression is crucial for model performance and optimization during predictions.