Embed presentation
Downloaded 27 times




![Discriminative vs Generative Models
● Discriminative models
○ Estimate conditional models P[Y | X]
○ Linear regression
○ Logistic regression
● Generative models
○ Estimates joint probability P[Y, X] = P[Y | X] P[X]
○ Not only probability of labels but also the features are estimated
○ LDA, QDA
○ Naive Bayes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-180913171224/75/Logistic-Regression-5-2048.jpg)








The document provides an overview of logistic regression, describing it as a classification technique used to predict categorical dependent variables by estimating probabilities. Key aspects of logistic regression covered include discriminative versus generative models, the assumptions of conditional independence and Gaussian distribution, and using maximum likelihood conditional estimation to solve the maximization problem through iterative methods like gradient descent. The document also distinguishes logistic regression from naive Bayes classification by directly learning the probability of the dependent variable given the independent variables.
Introduction to logistic regression, its goals, and importance in data science.
Overview of logistic regression, discriminative vs generative models, and Bayes' theorem.
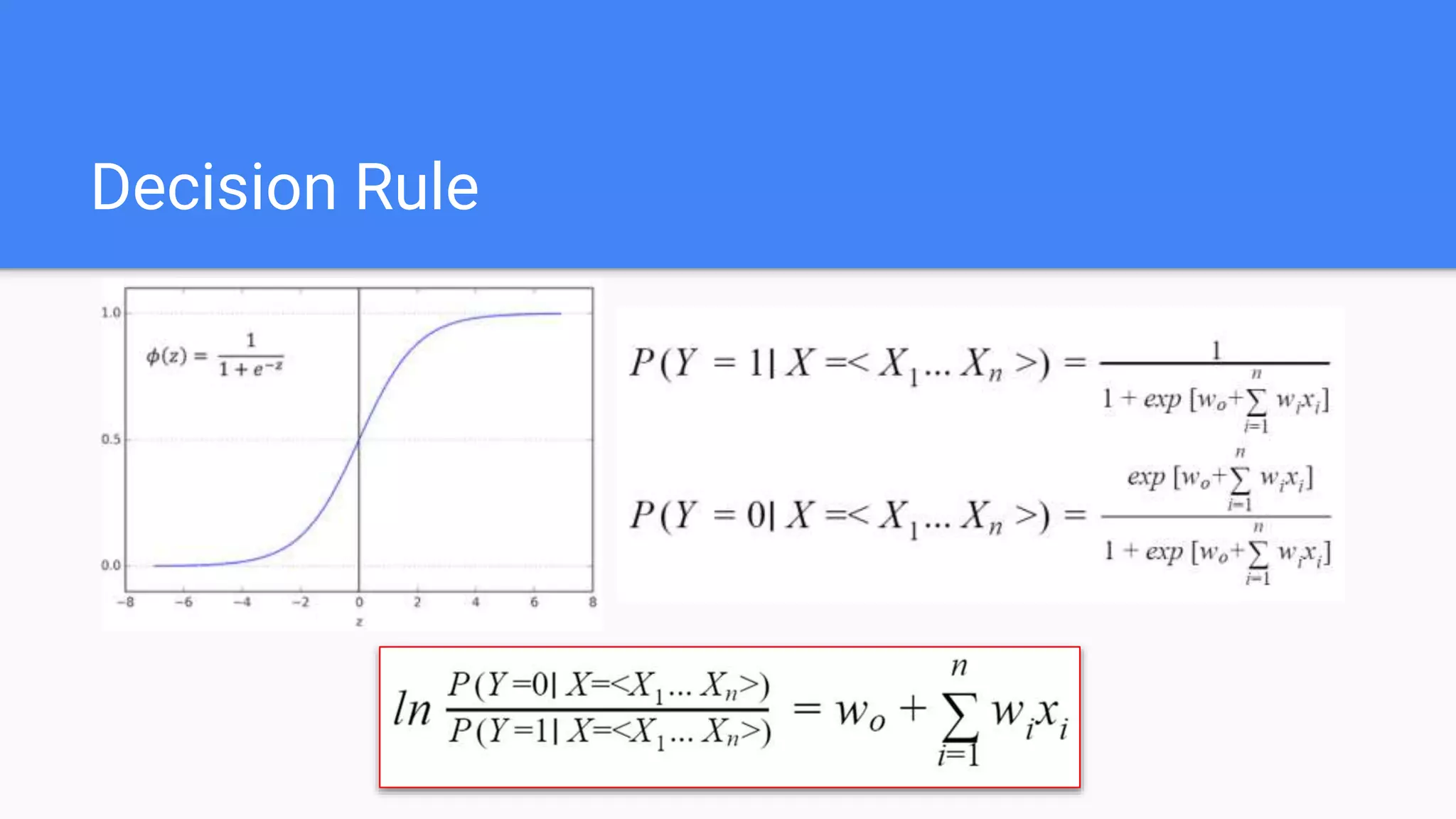
Mechanics of logistic regression including classifiers, assumptions of independence, and decision rules.
Optimization concepts like Maximum Likelihood Estimation, iterative methods, and multi-class classification.




![Discriminative vs Generative Models
● Discriminative models
○ Estimate conditional models P[Y | X]
○ Linear regression
○ Logistic regression
● Generative models
○ Estimates joint probability P[Y, X] = P[Y | X] P[X]
○ Not only probability of labels but also the features are estimated
○ LDA, QDA
○ Naive Bayes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-180913171224/75/Logistic-Regression-5-2048.jpg)







