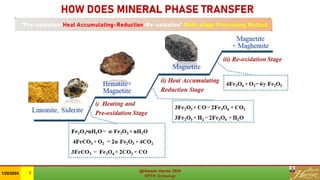
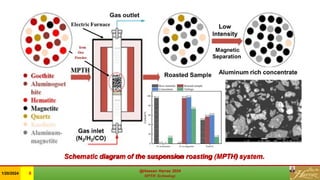
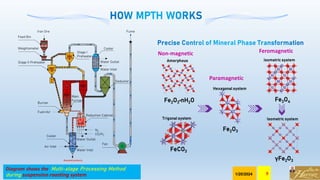
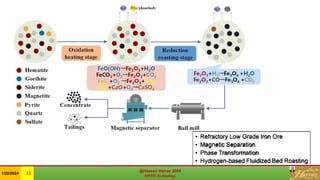
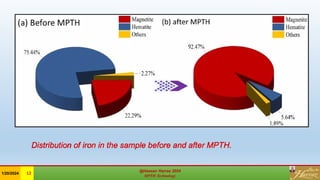
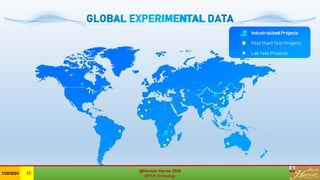
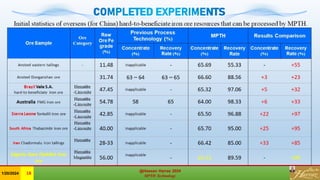
The document discusses the Minerals Phase Transformation by Hydrogen (MPTH) reduction technology, which offers an efficient method for processing hard-to-beneficiate iron ores and tailings. It highlights the economic and environmental advantages of MPTH in revitalizing low-grade iron ore resources and improving concentrate quality, particularly in the context of declining high-grade ore availability. Successful industrial applications and pilot projects demonstrate the technology's effectiveness in enhancing iron recovery and reducing sulfur content in concentrates.