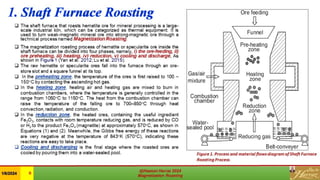
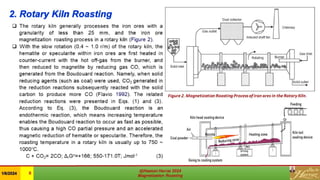
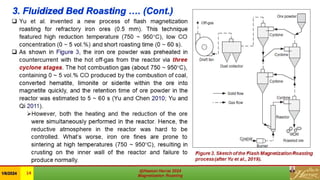
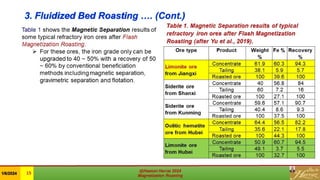
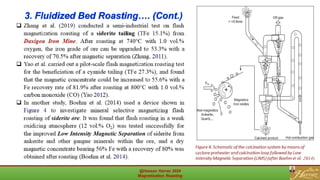
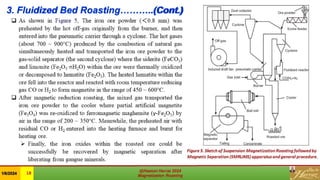
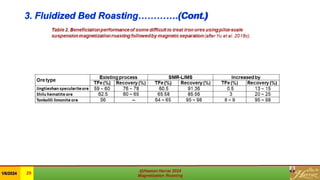
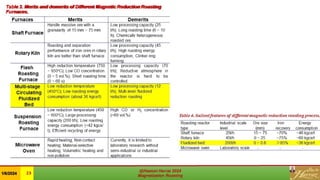
This document is a review of magnetization roasting methods for refractory iron ores, discussing various techniques such as shaft furnace roasting, rotary kiln roasting, fluidized bed roasting, and microwave-assisted roasting. It highlights the advancements and applications in mineral processing and extractive metallurgy over the past decade, along with a comparison of different methods. The document concludes with references to relevant studies and technological developments in the field.