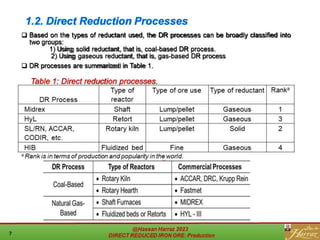
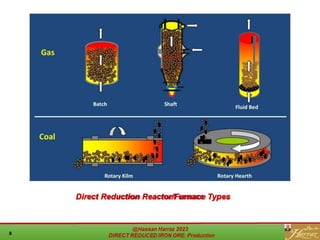
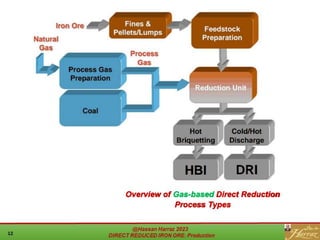
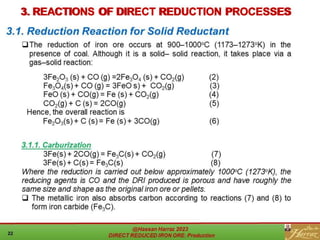
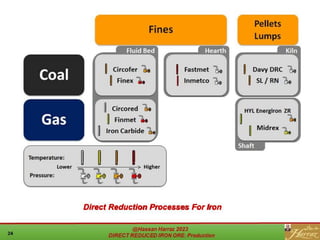
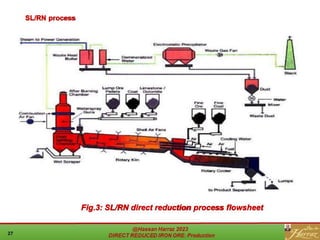
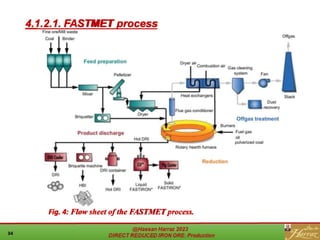
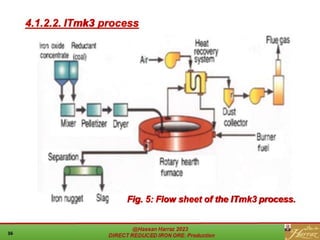
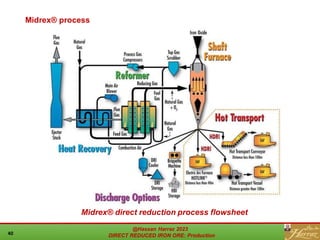
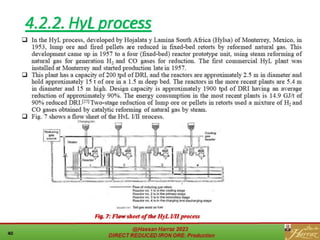
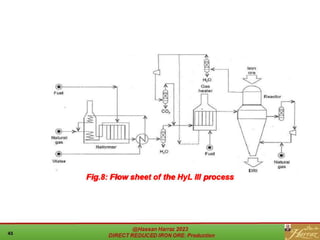
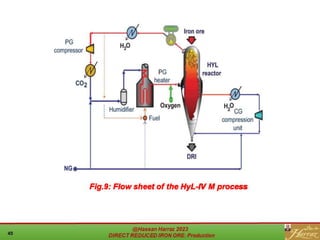
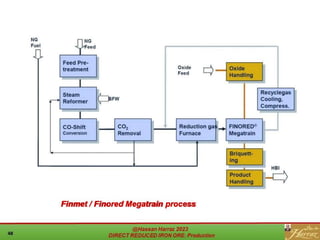
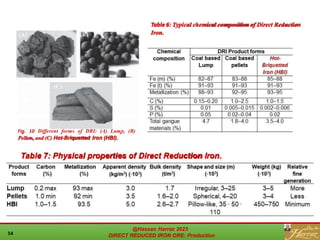
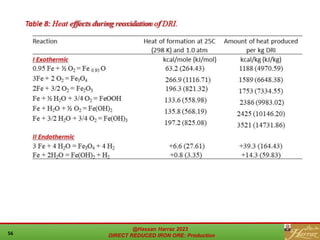
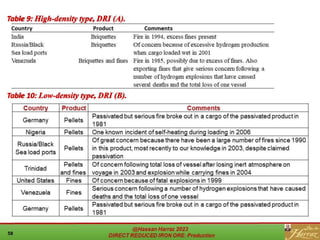
The document provides a comprehensive overview of direct reduced iron (DRI) production processes, including coal-based and gas-based methods. It details the raw materials, reactions involved, and characteristics of DRI, along with its transportation, storage, and various uses. The study emphasizes the environmental sustainability aspects and includes references for further reading.