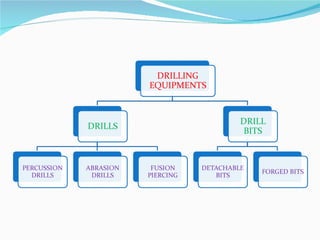
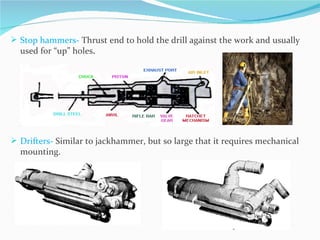
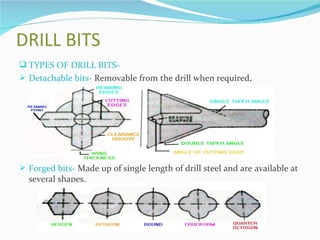
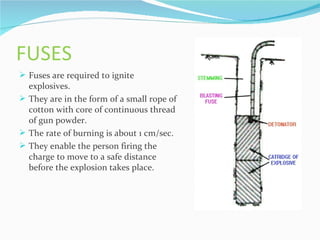
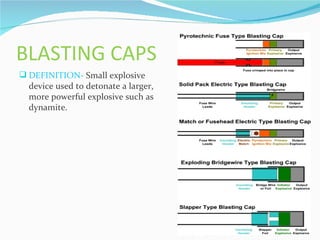
The document summarizes drilling and blasting equipment used in mining and construction. It describes various types of drills like percussion drills, abrasion drills, and fusion piercing. It also discusses components of drilling like drills, drill bits, and different drilling patterns. The document then explains the blasting process which involves using explosives like dynamite, detonators, fuses, and blasting caps. Proper handling and transportation of explosives is important for safety. The blasting procedure involves making blast holes, inserting charges, tamping, and detonating with a fuse or detonator.