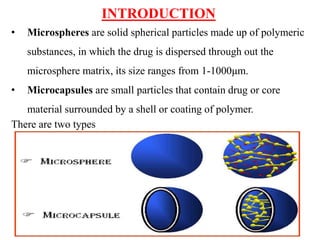
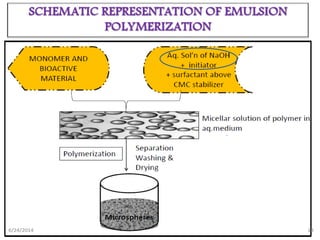
Microspheres are solid spherical particles made of polymers that can encapsulate drugs. They range in size from 1-1000μm. There are various methods for producing microspheres, including single and double emulsion techniques, polymerization methods, coacervation, spray drying, and solvent extraction. Microspheres offer advantages like controlled drug release, protection of unstable drugs, and targeting of specific tissues. They have various pharmaceutical applications including vaccine and drug delivery, with the ability to control release kinetics and target specific sites.