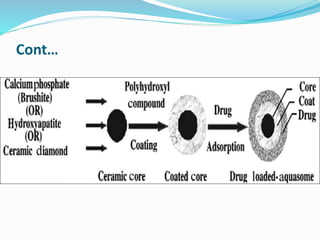
Aquasomes are nanoparticle carrier systems composed of a solid nanocrystalline core coated with polyhydroxy oligomers. They are able to protect fragile biological molecules through water-like properties and high surface exposure. Aquasomes are prepared through a self-assembly process involving interaction of charged groups, hydrogen bonding, and structural stability. This allows active loading of molecules like proteins, antigens, and genes. Characterization techniques confirm the structure, drug loading, and release kinetics of aquasomes, which have applications in delivery of vaccines, hemoglobin, insulin, and enzymes orally and intravenously.