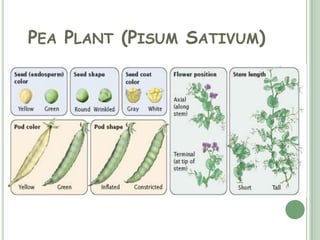
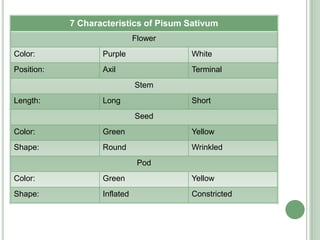
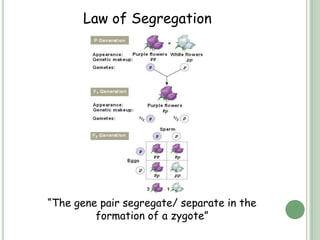
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian scientist who conducted breeding experiments with pea plants between 1856 and 1863. Through selective cross-breeding of pea plants over many generations, Mendel discovered that certain traits are inherited independently of each other and that traits can be dominant or recessive. Although the significance of Mendel's work was not recognized until the early 20th century, his experiments laid the foundation for modern genetics by demonstrating the basic principles of heredity and inheritance now known as Mendel's laws of inheritance.