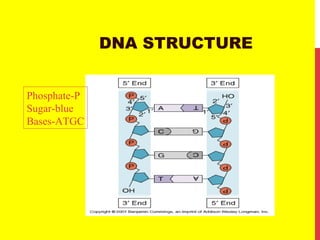
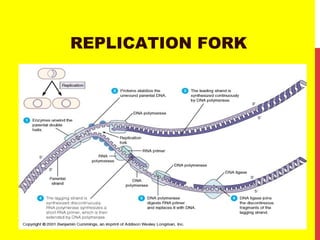
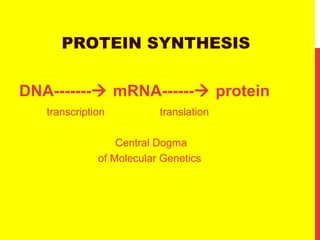
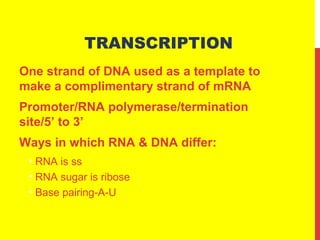
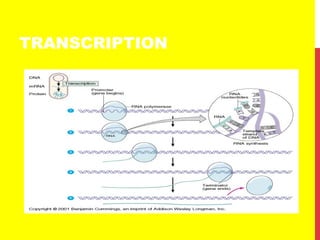
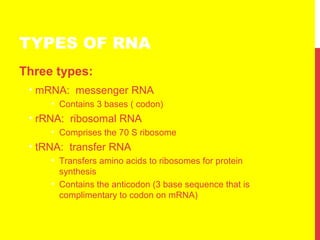
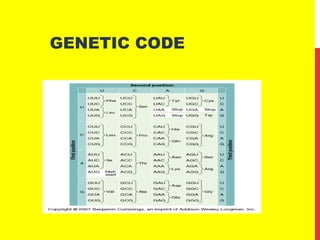
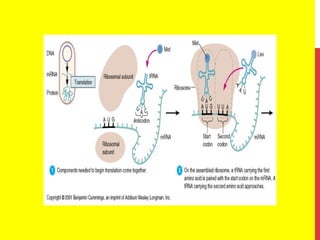
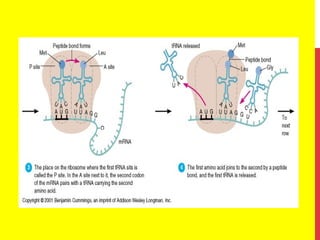
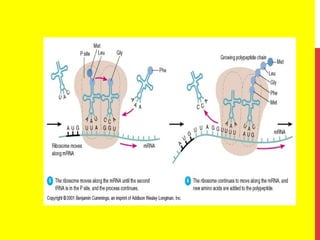
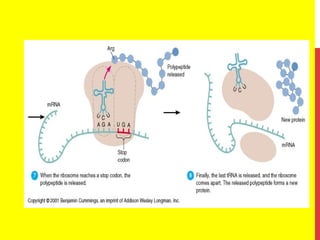
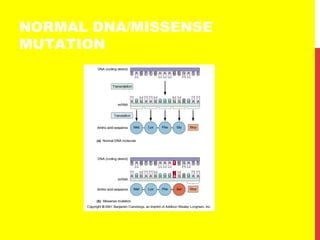
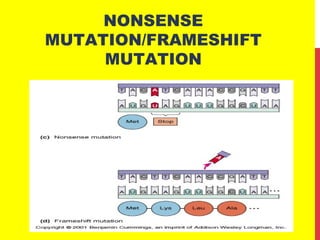
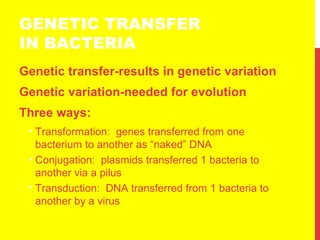
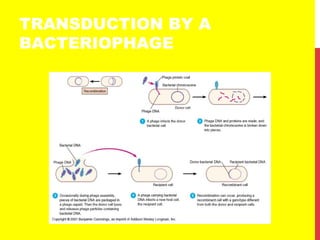
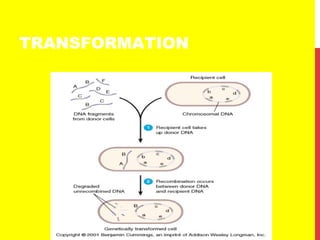
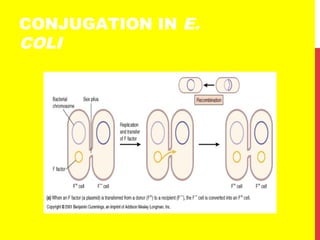
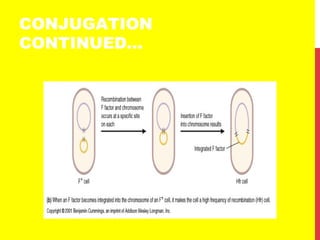
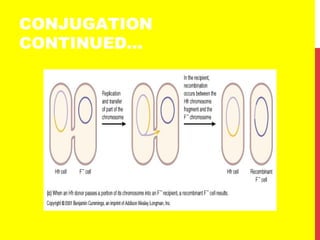
This document discusses the structure and function of genetic material in microbes. It covers the basics of DNA and RNA structure, DNA replication, transcription, translation, the genetic code, and mechanisms of genetic transfer in bacteria. DNA is made of nucleotides with a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base. It takes the form of a double helix. Bacterial DNA replication occurs via a replication fork that uses the parental DNA strands as templates. Transcription converts DNA into mRNA which is then translated into proteins. Mutation, transformation, conjugation, and transduction allow for genetic variation in bacteria.