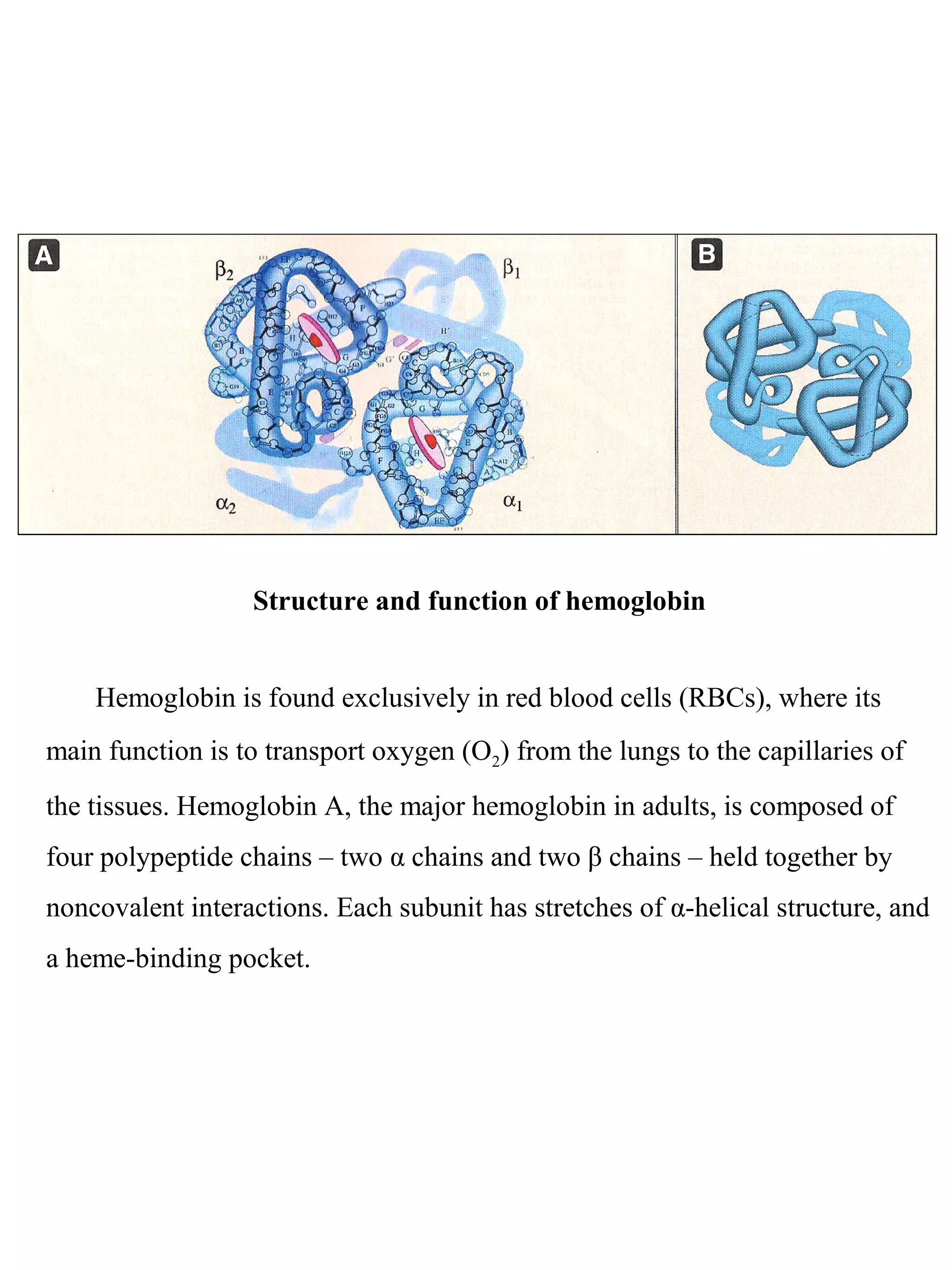
1. Hemoglobin transports oxygen in red blood cells through a cooperative binding mechanism between its four subunits. Each subunit contains a heme group that reversibly binds oxygen.
2. In tissues, higher carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion concentrations cause hemoglobin to release oxygen. However, in the lungs where oxygen levels are high, hemoglobin becomes saturated with oxygen.
3. Sickle cell anemia results from a mutation where glutamate is replaced by valine in the beta chain of hemoglobin. This causes deoxygenated hemoglobin to polymerize and distort red blood cells into a sickle shape, blocking blood flow.
































![[CH3-(CH2)10-CH2-O-SO3
-
]Na+
– sodium dodecyl sulfate SDS-treated
protein stend to have identical charge-to-mass ratios and similar shapes.
SDS-PAG ELECTROPHORESIS
The SDS – polyacrylamide
electrophoresis pattern of the
supernatant (left) and membrane
fractions (right) of various strains of
the Salmonella typhimurium. Samples
of 200-µg of protein each were run in
parallel lanes on a 35-cm - long x 0.8-
mm-thick slab gel containing 10%
polyacrylamide. The lane marked
MW contains molecular weight
standards.
A logarithmic plot of the
molecular masses of 37 different
polypeptide chains ranging from
11 to 70 kD versus their relative
electrophoretic mobilities on an
SDS-polyacrylamide gel.
Many proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain → SDS
treatment disrupt the noncovalent interactions between these subunits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinsandtheirbiologicalstructures-160316162521/75/Proteins-and-their-biological-structures-37-2048.jpg)
