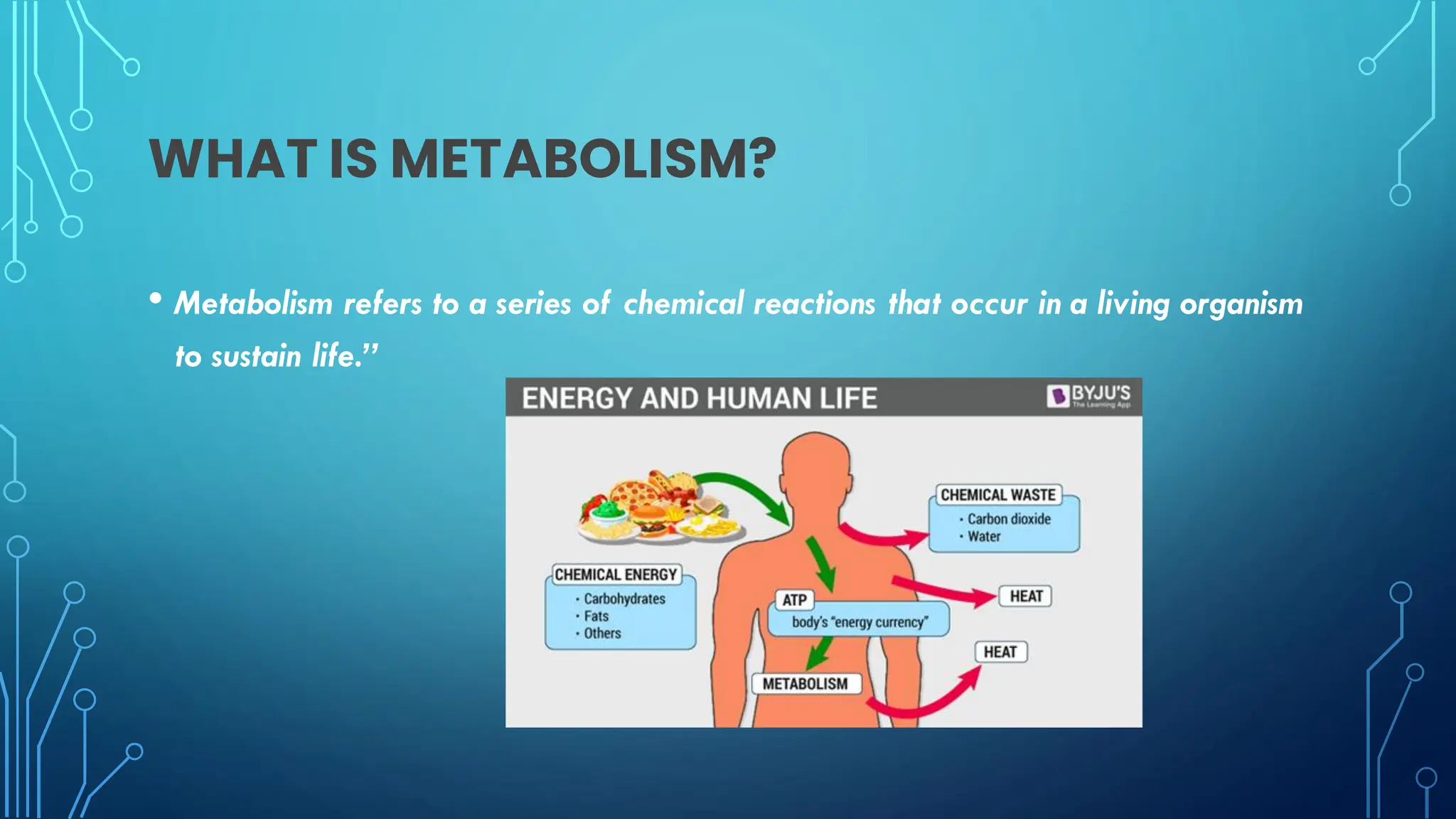
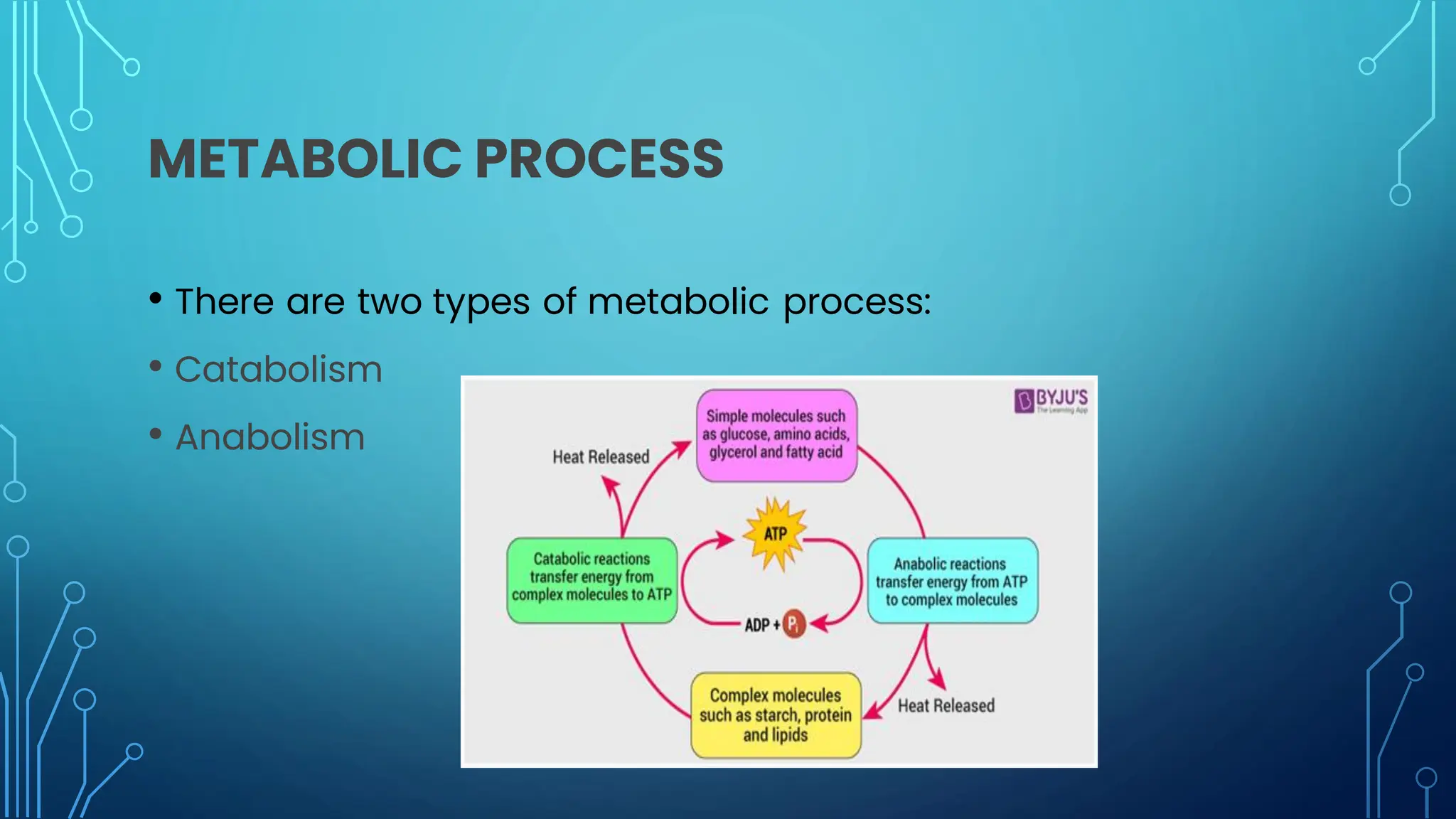
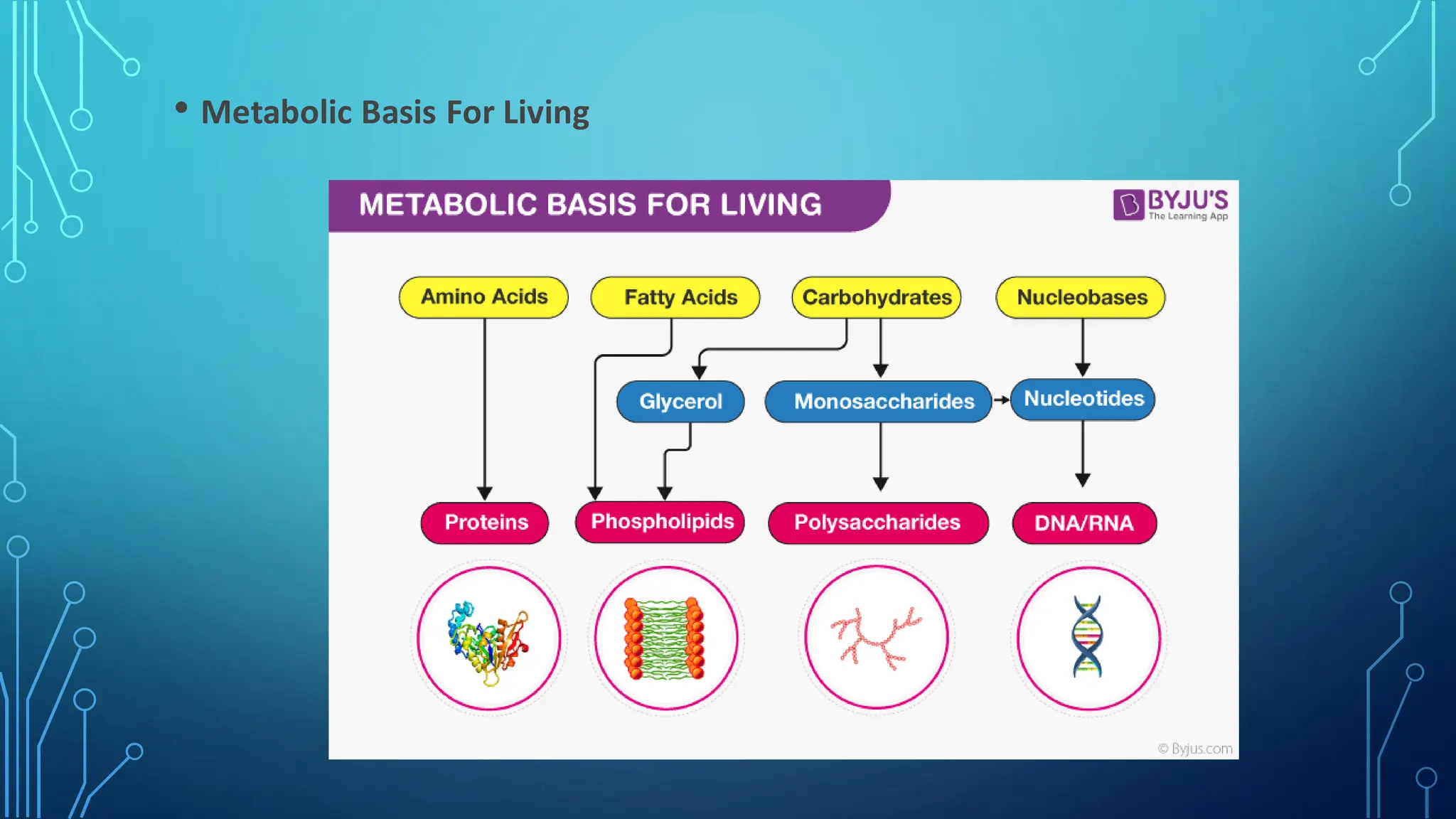
The document discusses various aspects of metabolism, including the two main types of metabolic processes (catabolism and anabolism), how organisms obtain energy through the breakdown of nutrients like carbohydrates and proteins, and factors that can increase metabolic rate such as caffeine, fiber, and organic foods. It also covers topics like microbial metabolism, nitrogen fixation by microbes, aerobic and anaerobic respiration, and the role of metabolism in sustaining life.