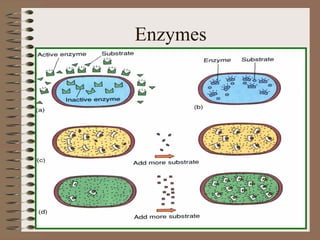
This document discusses the physiology and metabolism of bacteria. It explains that bacteria metabolize organic and inorganic substrates to generate energy through catabolic pathways, while using this energy for anabolic pathways to synthesize cellular components. The four main components of bacterial cells are water, organic matter like proteins and carbohydrates, and inorganic minerals. Bacteria are classified based on their nutritional requirements, oxygen usage, and optimal temperature for growth. Enzymes play a key role in bacterial metabolism by catalyzing biochemical reactions. Bacterial growth occurs through binary fission and follows a characteristic growth curve with lag, logarithmic, stationary, and death phases.