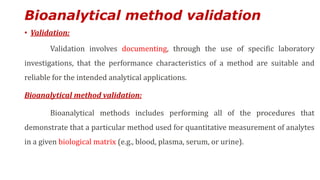
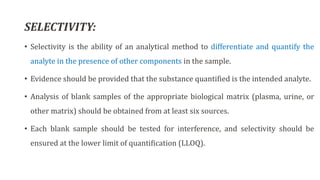
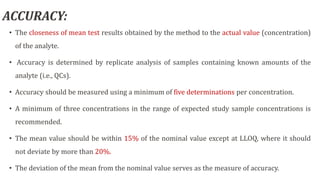
This document outlines USFDA guidelines for bioanalytical method validation. It discusses the objectives of method development which are to accurately and precisely quantify analytes under given laboratory conditions. The steps in method development include literature review, technique identification and optimization, reference standard preparation, and more. It also describes the types of validation including full, partial, and cross validation. The key validation parameters that must be evaluated and criteria that must be met are selectivity, accuracy, precision, recovery, calibration curves, sensitivity, reproducibility, and stability.