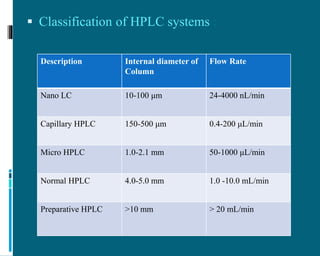
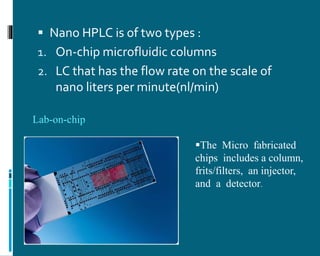
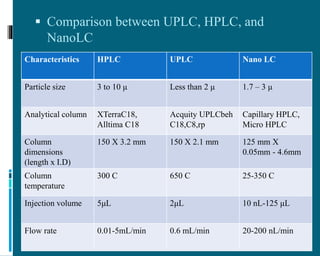
The document discusses the advancements and applications of nano liquid chromatography (NLC) and ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) in pharmaceutical and biological analysis. NLC is notable for its high sensitivity and efficiency, reducing mobile phase consumption, particularly aiding proteomics research, while UPLC enhances resolution and speed of analysis at high pressures. Both techniques offer significant advantages over traditional HPLC, with various applications ranging from drug discovery to environmental sample analysis.