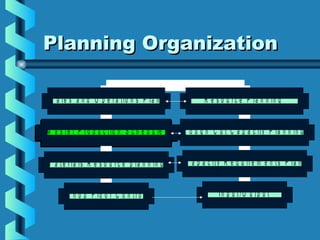
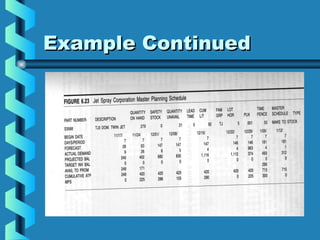
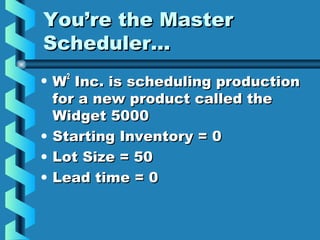
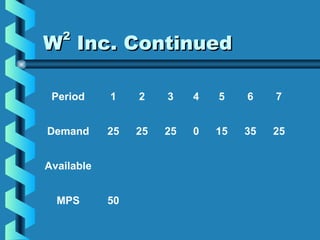
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) breaks down the production plan into product families to promote valid order promises and control inventory levels. It disaggregates sales and operations data and schedules production to meet demand while accounting for factors like lot sizes, lead times, and available inventory. By validating capacity and scheduling production proactively, the MPS enables a company to maintain desired levels of customer service while proactively controlling resources and inventory.