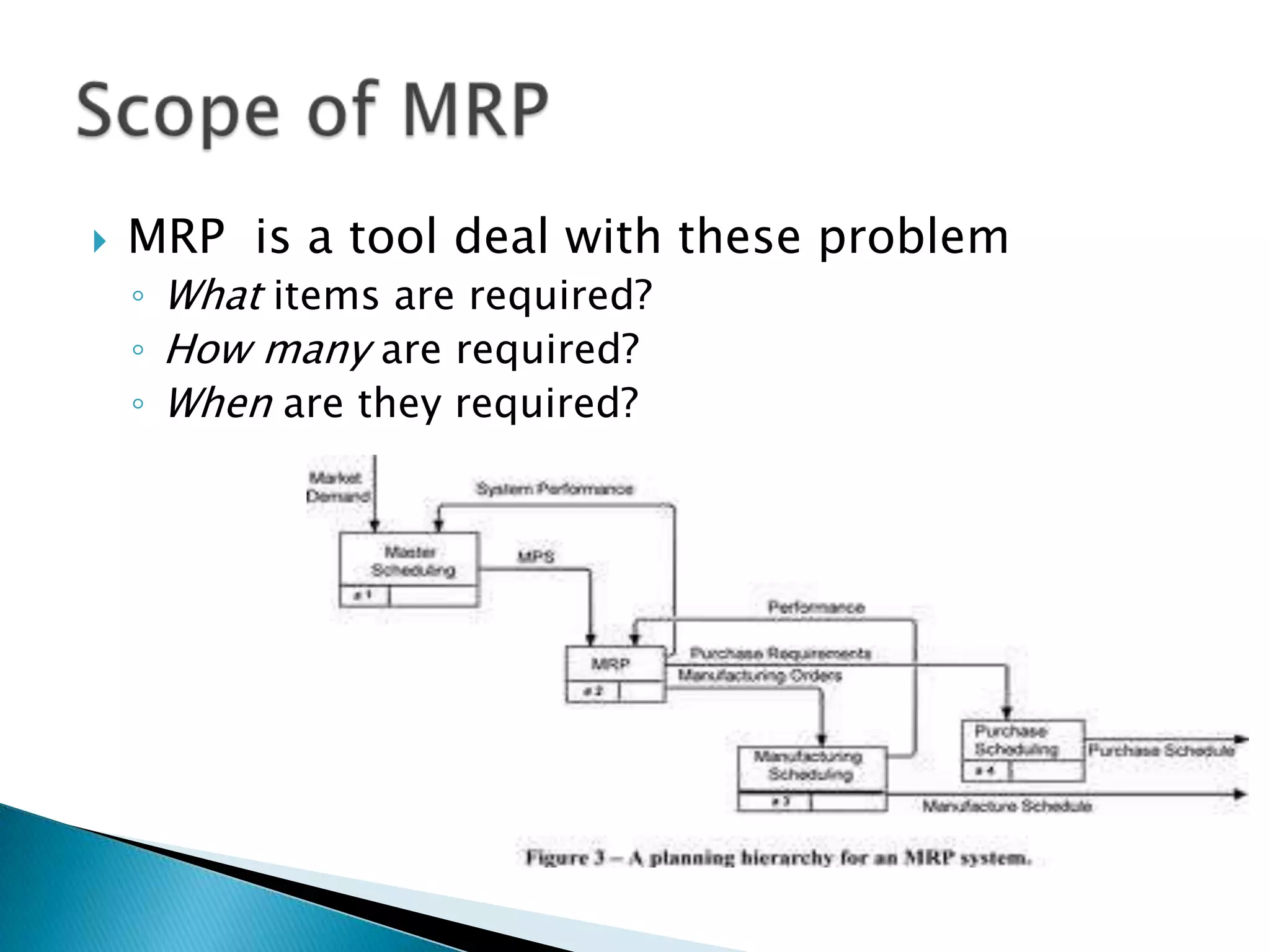
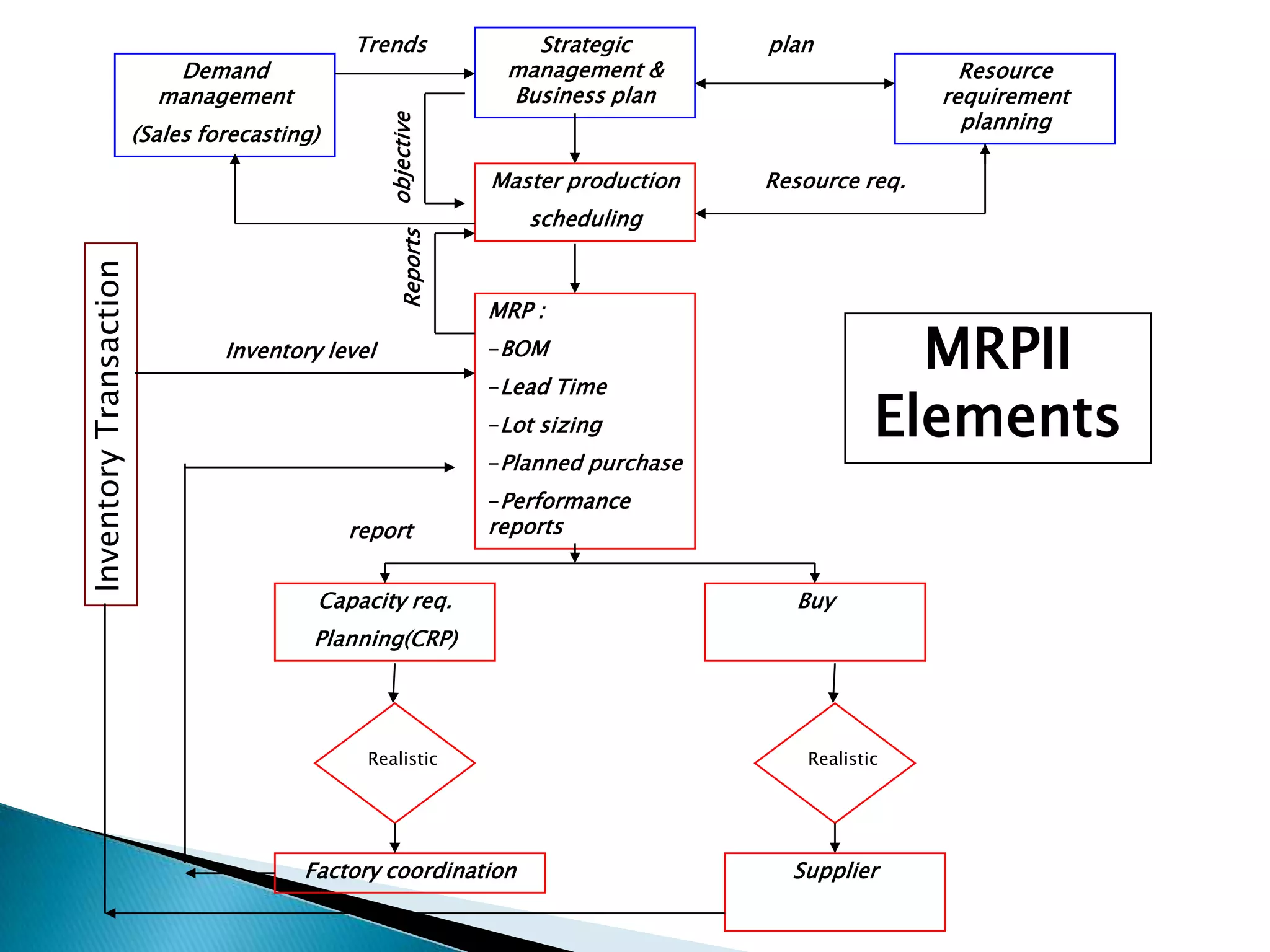
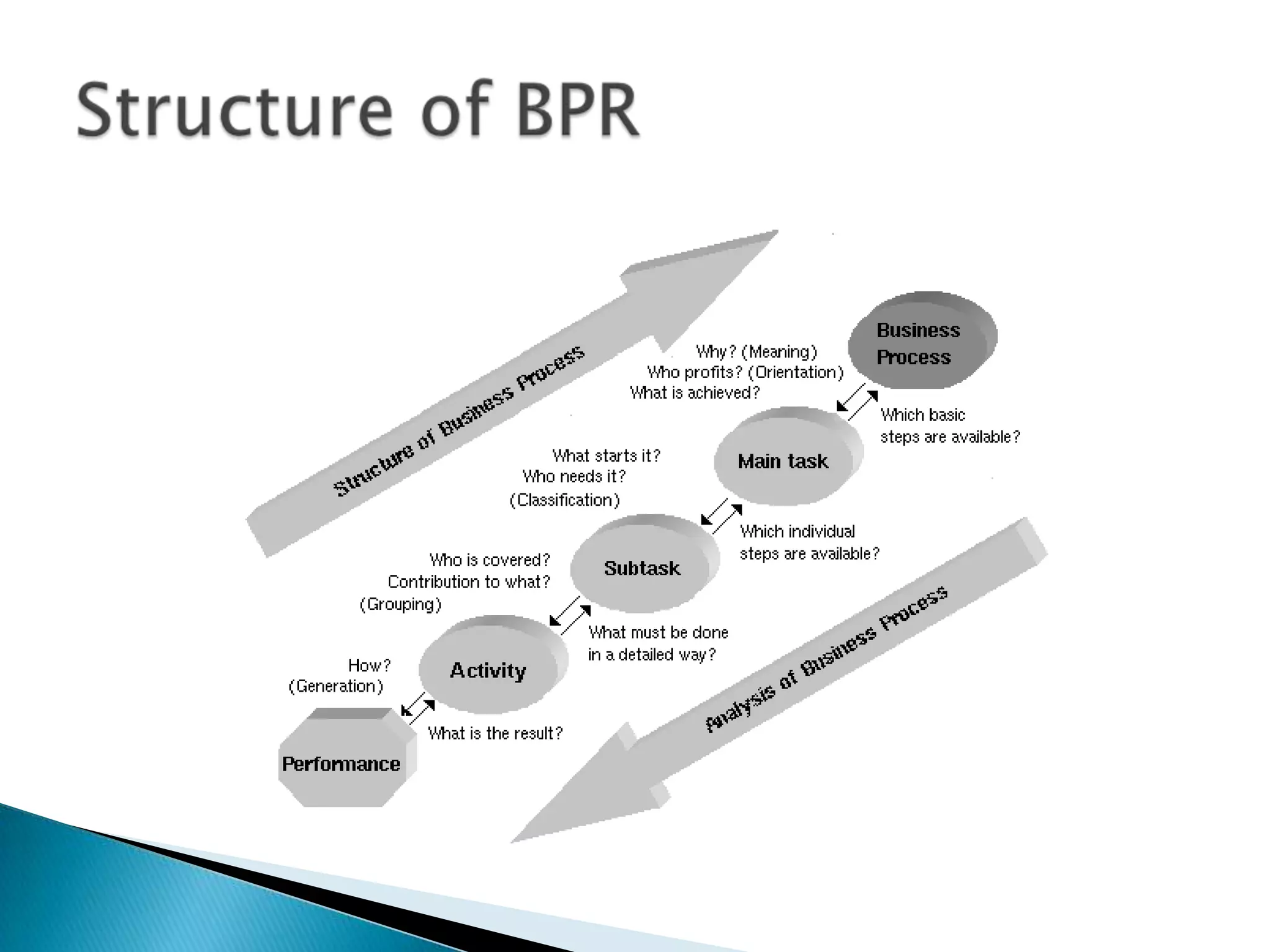
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. MRP uses a computer to help manage materials and inventories by creating material plans and production schedules based on supply chain lead times. MRP systems require accurate data including a master production schedule, bill of materials, lead times, and inventory balances to function effectively and produce useful outputs for meeting production needs.