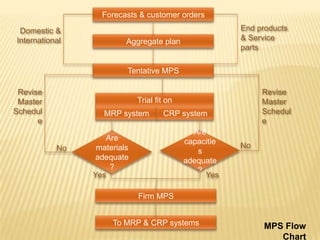
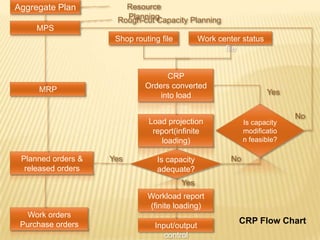
Operations planning involves organizing a manufacturing system to efficiently convert inputs into finished products. Production planning considers factors like production volume, processes, and operations. There are different manufacturing approaches like make-to-order or make-to-stock. Planning has strategic, tactical, and operational levels over different time spans. The master production schedule sets quantities to complete over a short horizon by reviewing forecasts, orders, and capacity. Material requirements planning determines needed components to produce finished products as scheduled. Capacity requirements planning ensures adequate labor and equipment to meet production objectives.