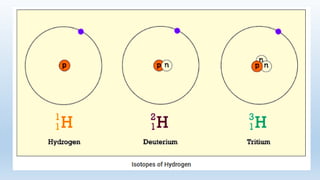
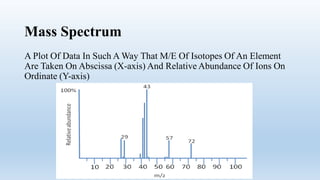
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the exact masses and relative abundance of isotopes, as well as molecular masses and structures. It involves a series of steps including vaporization, ionization, acceleration, deflection, and collection, whereby substances are converted to vapor, ionized, and their ions separated based on mass-to-charge ratios. Historically, significant developments include Aston's mass spectrograph and Dempster's mass spectrometer, which advanced the study and identification of isotopes.