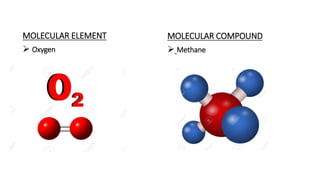
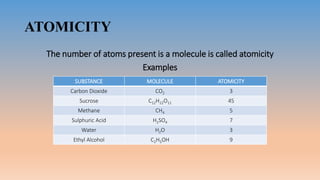
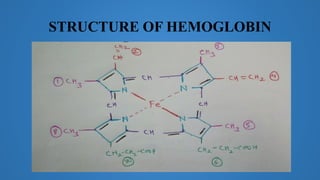
The document discusses molecules and their classification. It defines a molecule as the smallest particle of a pure substance that can exist independently. Molecules can be molecular elements like oxygen or molecular compounds like methane. Molecules exist independently because they are formed by the combination of unstable atoms that become stable. Molecules are classified based on atomicity, nature, and size. Atomicity refers to the number of atoms in a molecule. Nature describes if a molecule contains the same (homoatomic) or different (heteroatomic) atoms. Size can be micro-molecules that are simple and exist as monomers, or macro-molecules that are large polymers like hemoglobin, starch, and cellulose. Hemoglobin in particular is