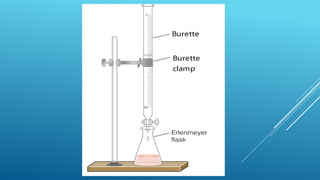
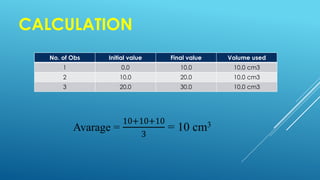
The document discusses volumetric analysis in chemistry, specifically focusing on titration, which is a method for determining the concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. It details important terms, types of titration, necessary apparatus, and the procedural steps involved. Additionally, it emphasizes safety precautions and provides formulas for calculating molarity and strength.