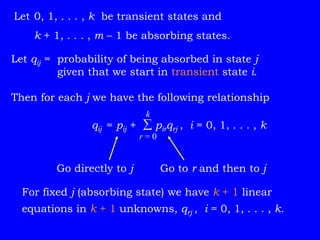
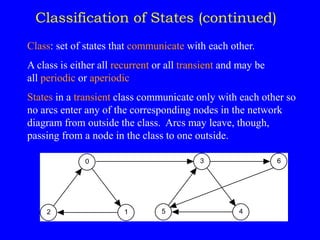
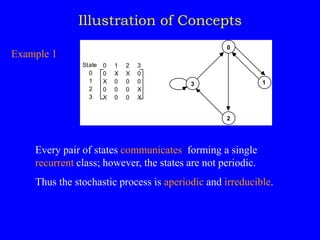
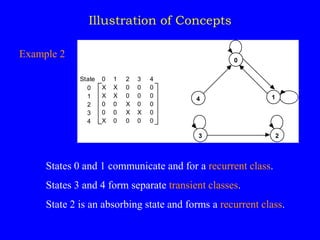
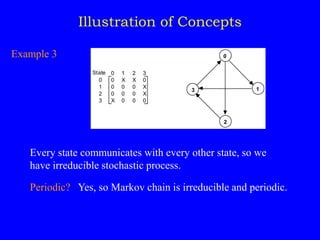
This document discusses additional topics related to discrete-time Markov chains, including:
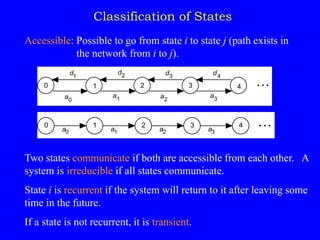
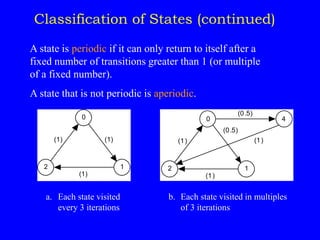
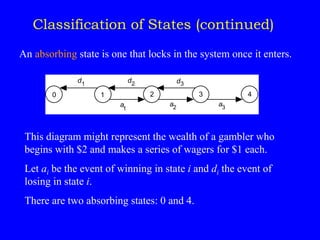
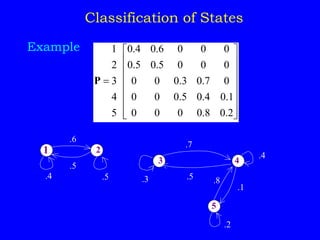
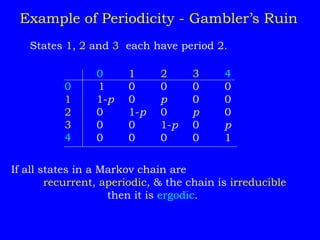
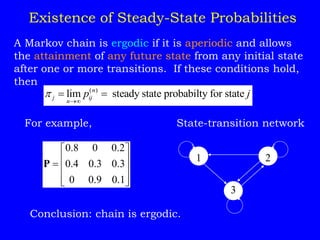
1) Classifying states as recurrent, transient, periodic, or aperiodic;
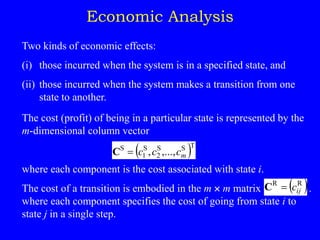
2) Economic analysis of Markov chains by considering costs of states and transitions;
3) Calculating first passage times and steady-state probabilities.
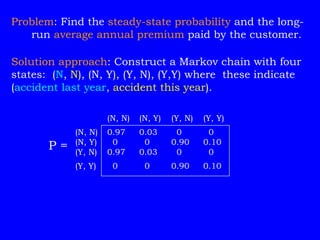
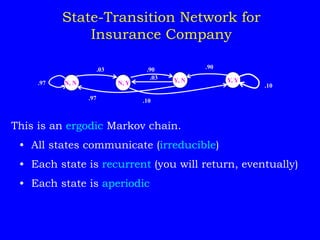
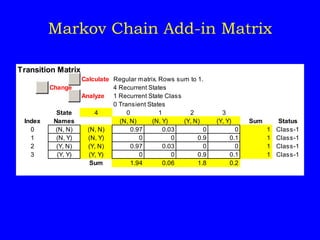
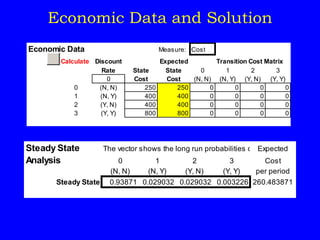
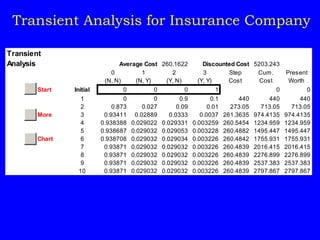
As an example, it analyzes an insurance company Markov chain model with four states representing customer accident history to find the long-run average annual premium.






![Expected Cost for Markov Chain
Expected cost of being in state i: ij
m
j
ij
i
i p
c
c
c
1
R
S
Let C = (c1, . . . cm)T
ei = (0, 0, 1, 0, 0) be the ith row of the m m identity
matrix, and
fn = a random variable representing the economic return
associated with the stochastic process at time n.
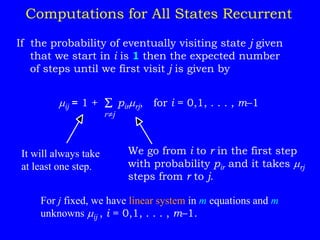
Property 3: Let {Xn : n = 0, 1, . . .} be a Markov chain with finite
state space S, state-transition matrix P, and expected
state cost (profit) vector C. Assuming that the process
starts in state i, the expected cost (profit) at the nth step
is given by
E[fn(Xn) |X0 = i] = eiP
(n)
C.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markovchain-220909160257-e423468b/85/markov-chain-ppt-18-320.jpg)
![Additional Cost Results
What if the initial state is not known?
Property 5: Let {Xn : n = 0, 1, . . .} be a Markov chain with finite
state space S, state-transition matrix P, initial
probability vector q(0), and expected state cost (profit)
vector C. The expected economic return at the nth step
is given by
E[fn(Xn) |q(0)] = q(0)P
(n)
C.
Property 6: Let {Xn : n = 0, 1, . . .} be a Markov chain with finite
state space S, state-transition matrix P, steady-state
vector π, and expected state cost (profit) vector C. Then
the long-run average return per unit time is given by
SiS πici = πC.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markovchain-220909160257-e423468b/85/markov-chain-ppt-19-320.jpg)