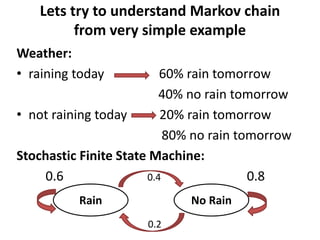
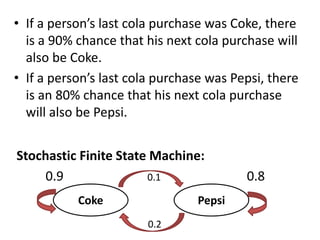
This document presents a summary of the Markov chain model. It begins with an introduction to development planning models and an overview of the Markov chain model and its properties. It then discusses the origin of Markov chains and how they were introduced by Andrey Markov. Several applications of Markov chain models are provided, such as market research, text generation, and customer journey predictions. Finally, the document concludes with a simple example of using a Markov chain to model weather patterns.