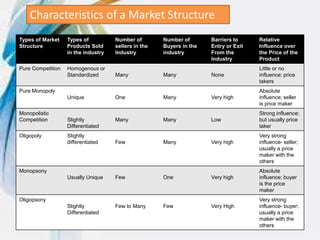
This document defines and classifies different market structures. The main market structures discussed are perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition. Perfect competition is characterized by many small sellers, standardized products, and no single seller influencing prices. A monopoly has a single seller dominating an industry. Oligopoly has a few large sellers controlling the market. Monopolistic competition involves differentiated but similar products among many sellers. The document also briefly discusses monopsony and oligopsony structures defined by a single or few dominant buyers.