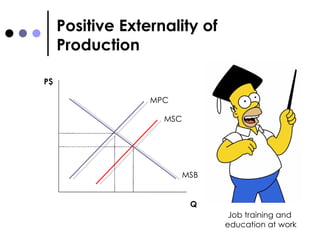
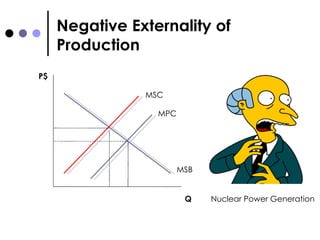
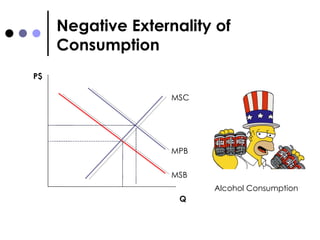
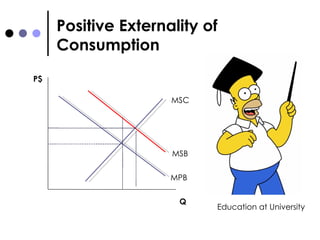
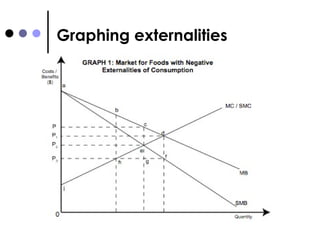
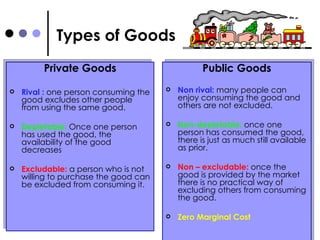
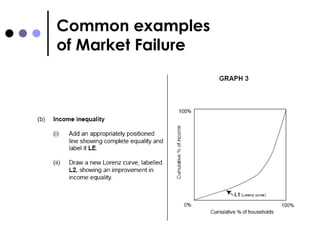
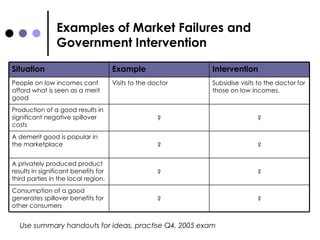
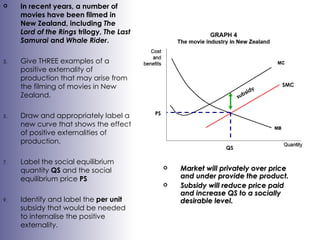
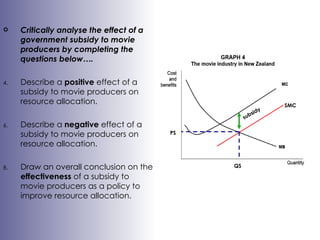
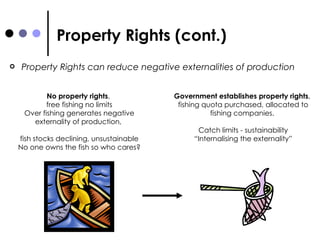
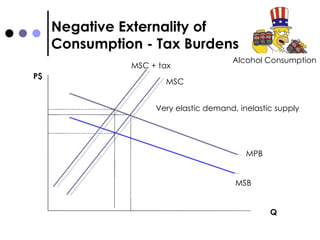
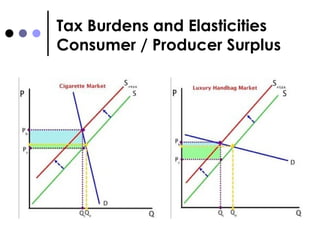
The document discusses market failures and government interventions to address them. It provides examples of market failures such as pollution, traffic congestion, and underprovision of public goods. It also lists government policy tools like taxes, subsidies, and regulations that can be used to correct market failures and achieve more efficient resource allocation.