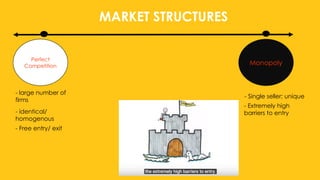
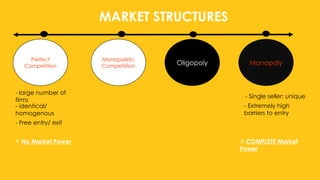
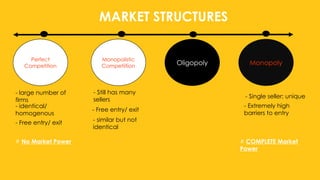
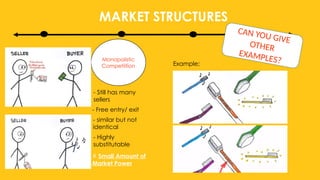
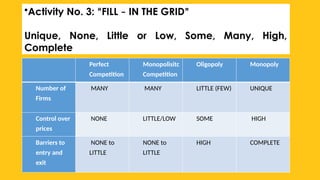
The document outlines the four main types of market structures: perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly, detailing their characteristics and differences. It includes activities for students to engage with these concepts, such as simulations and grid completions. The key takeaway is that market structures affect competition levels, prices, and production quantities of goods and services.