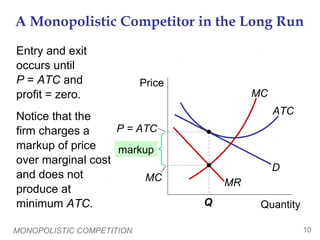
This document discusses monopolistic competition as a market structure between perfect competition and monopoly. Key points include:
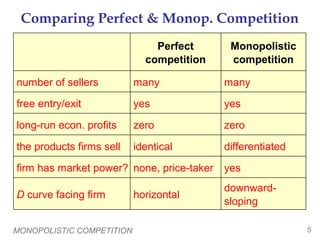
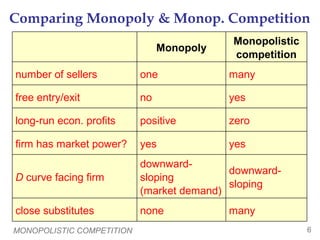
- Under monopolistic competition, many firms sell differentiated products and free entry leads to zero long-run economic profits.
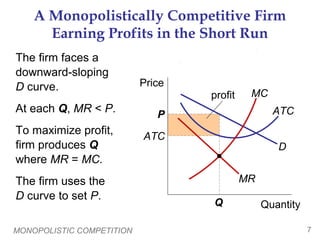
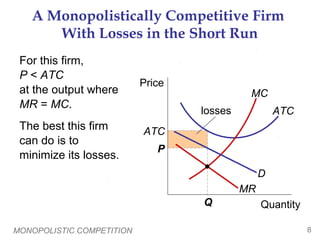
- Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve and can set prices above marginal cost in the short-run. In the long-run, entry drives prices down to average total cost.
- Compared to perfect competition, monopolistic competition results in excess capacity and prices above marginal cost, reducing efficiency. However, policy solutions are difficult given firms earn zero profits.
- Product differentiation encourages advertising and branding, which have debated social costs and benefits in terms of competition and consumer information.