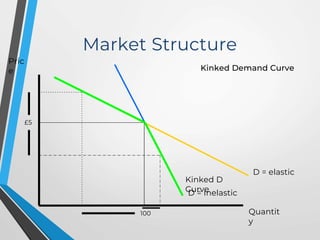
This document discusses different market structures and their characteristics. It describes perfect competition as having many small firms, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and price-taking behavior. Monopolistic competition features product differentiation and monopolies have significant barriers to entry allowing them to control price or supply. Oligopolies are markets dominated by a small number of large firms with interdependent behavior. The type of market structure influences pricing, supply, competition and efficiency.