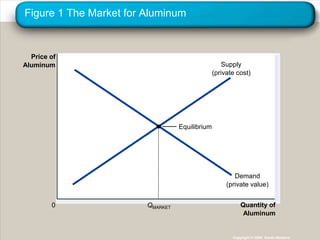
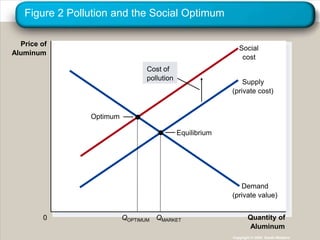
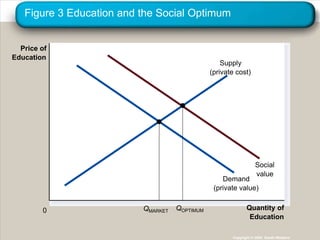
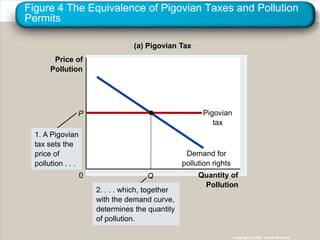
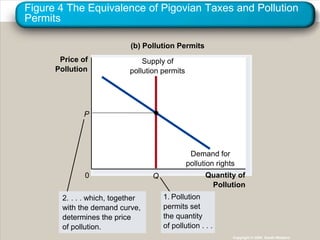
This document discusses externalities and how they can lead to market inefficiencies. It defines externalities as uncompensated impacts of one person's actions on another. Negative externalities like pollution lead to overproduction, while positive externalities like education benefits lead to underproduction. Government policies like Pigouvian taxes or tradable permits can help internalize these externalities and achieve socially optimal production levels. Private solutions via bargaining are also possible using the Coase theorem, but transaction costs may prevent private solutions in some cases.