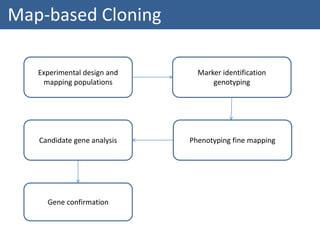
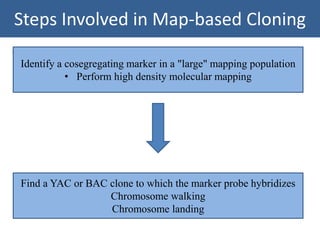
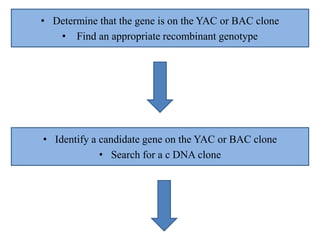
The document summarizes the process of map-based cloning, also called positional cloning. It describes how researchers used genetic mapping and linkage analysis to clone the Pto gene in tomato, which provides resistance to bacterial speck disease. The key steps included identifying a molecular marker closely linked to the Pto gene, screening a YAC library to find a clone containing the gene region, identifying candidate genes on the clone, and ultimately transforming plants to show that one candidate gene, CD186, rescued the wild-type phenotype when introduced into susceptible plants.






![• Recently map-based cloning was employed to clone the first
plant resistance gene that follows the gene-for-gene
interaction.
• The tomato gene that was cloned was Pto and it provides
resistance against bacterial speck disease of tomato caused
by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato.
• This pathogen expresses the avirulence gene avrPto that
interacts with Pto to provide resistance in tomato. This gene
was cloned by Martin et al. [Science (1993) 262:1432]..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mapbasedcloning-231002124636-f295aed8/85/Map-Based-Cloning-pptx-13-320.jpg)




