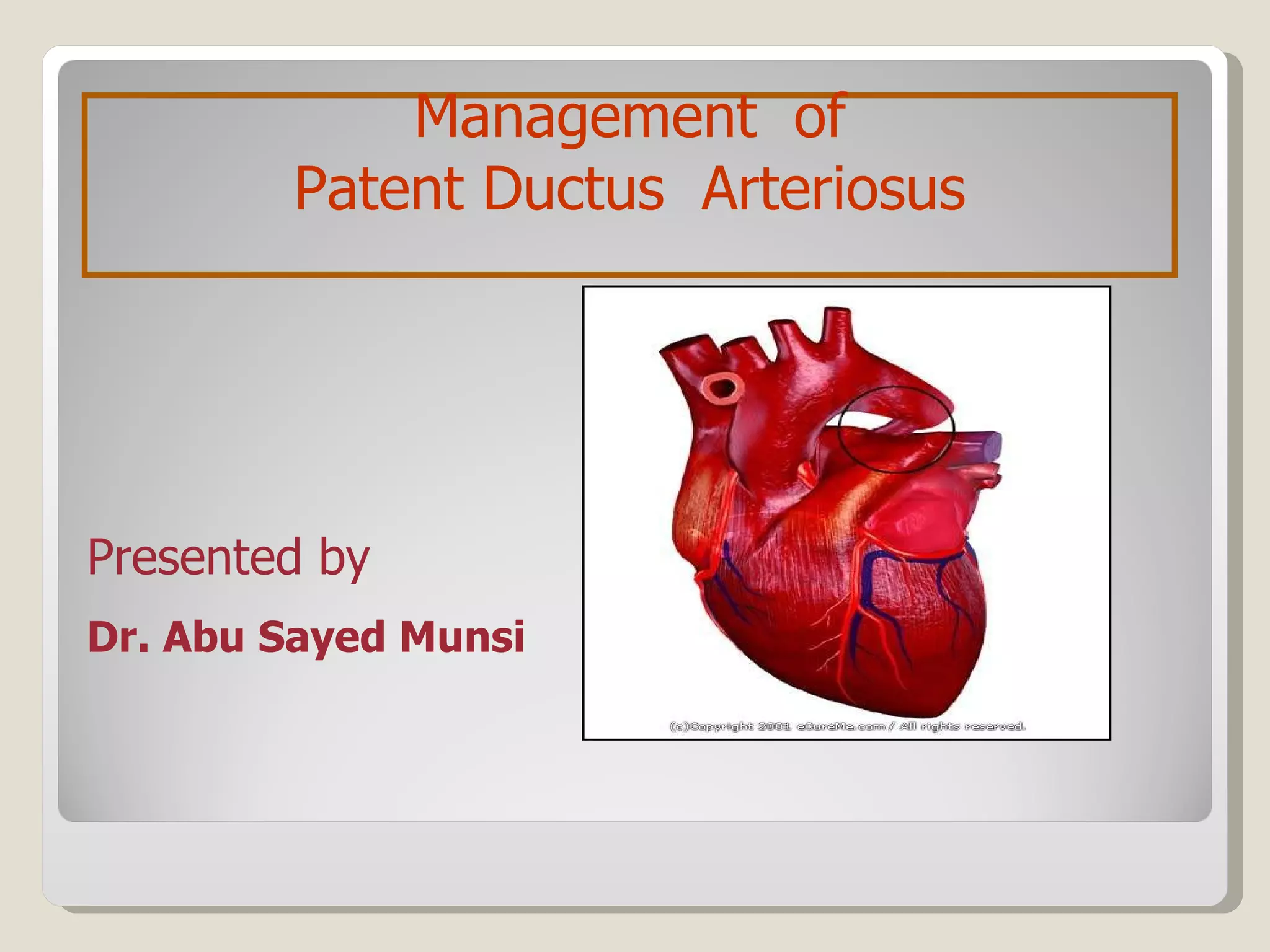
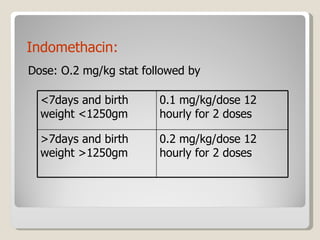
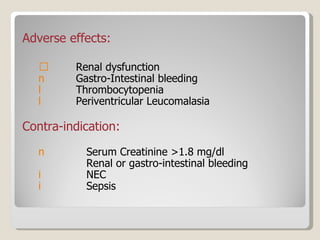
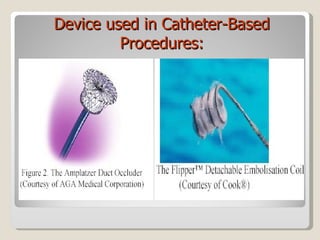
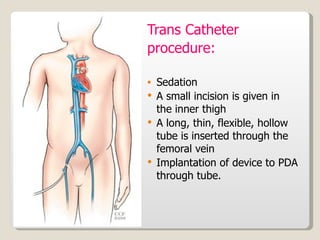
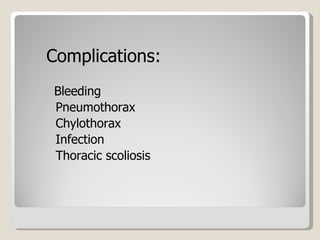
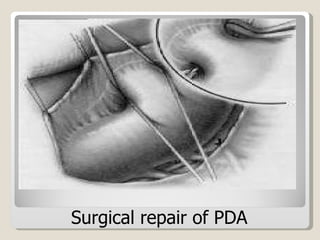
The document discusses treatment options for patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in infants. There are three main options: medical management using drugs like indomethacin or ibuprofen, catheter-based procedures to close the PDA, or surgical intervention. Medical management is usually the first approach using anti-inflammatory drugs and involves balancing treatment against potential renal or gastrointestinal side effects. If medical management fails, catheter or surgical closure may be considered, with catheter procedures preferred if the PDA is suitable due to lower risks. Surgical ligation is an option when other approaches are not viable or have failed.