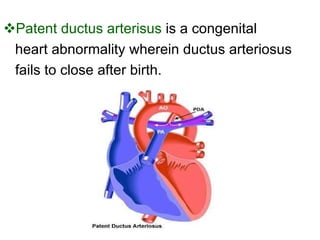
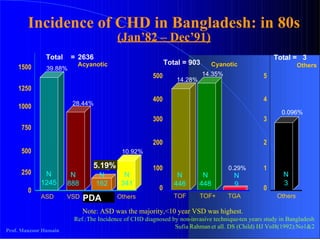
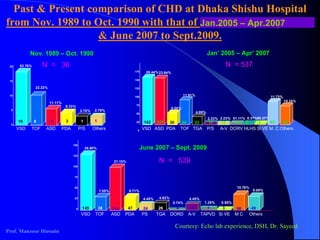
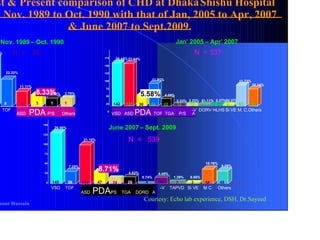
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect where the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth. It occurs in approximately 1 in 2000 full term infants and 8 per 1000 premature births. The incidence is higher in preterm infants, with rates of 50-80% in infants under 26 weeks gestation. If left untreated, PDA has a mortality rate of 20% by age 20, 45% by age 45, and 60% by age 60.