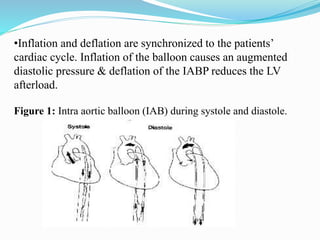
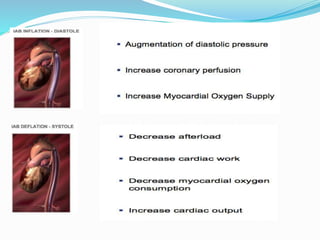
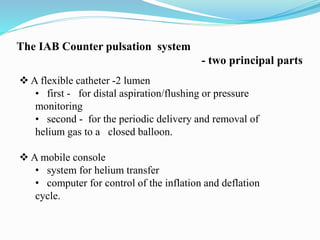
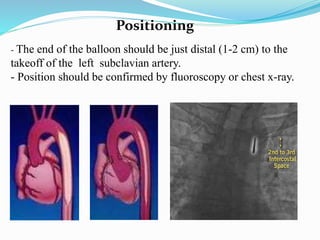
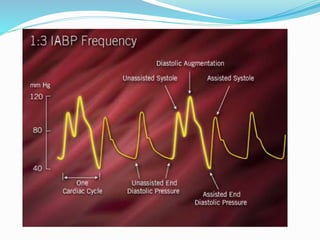
The document provides information about intra-aortic balloon pumps (IABP). It discusses that IABPs were first described in 1958 and have since improved. IABPs provide temporary left ventricular support by displacing blood in the aorta. They work by inflating in diastole and deflating before systole to increase cardiac output and coronary perfusion pressure while decreasing workload. IABPs are used for cardiac failure, unstable angina, postoperative complications, and as a bridge to transplantation. Complications include limb ischemia, bleeding, thrombosis, and infection.