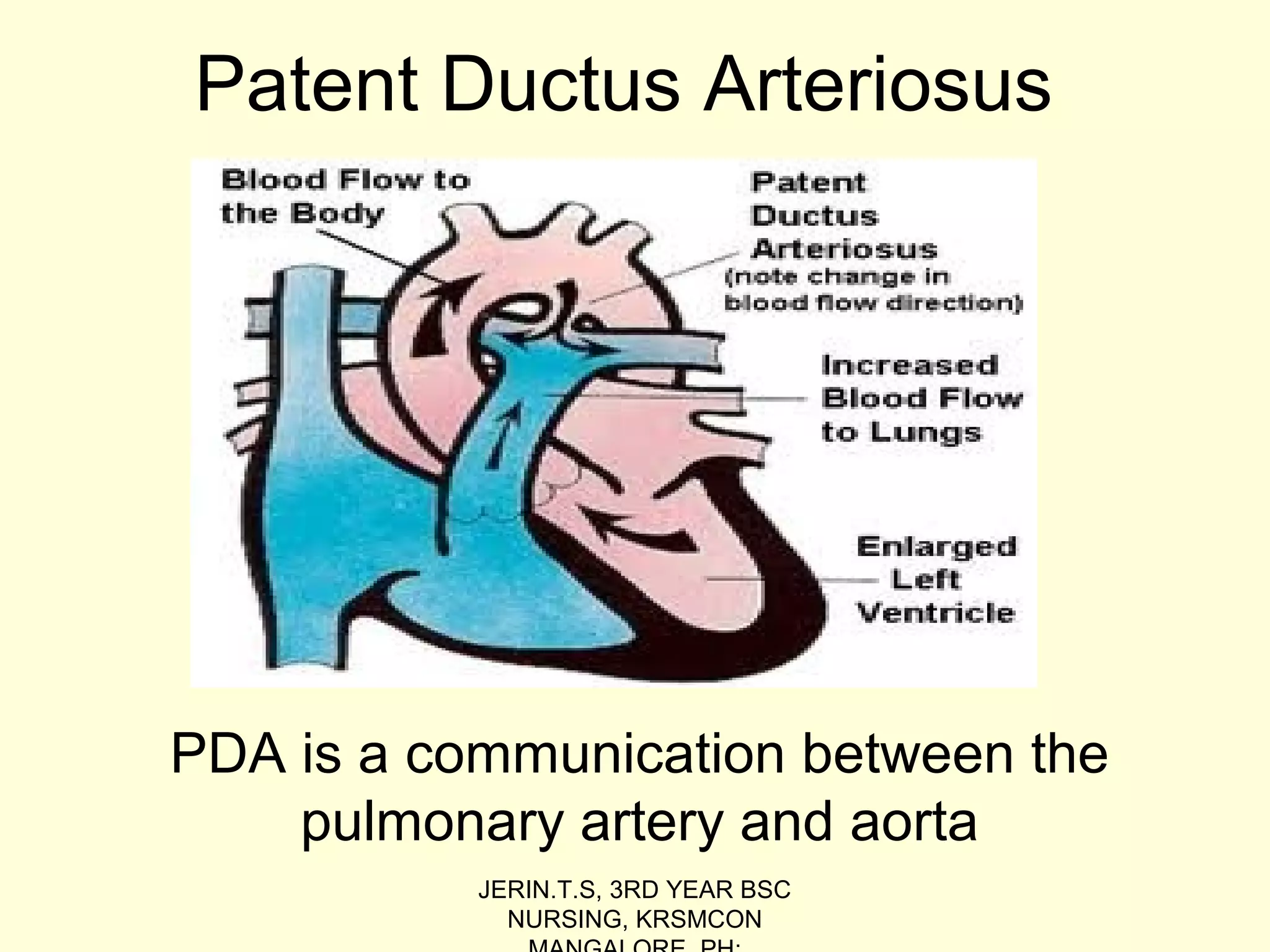
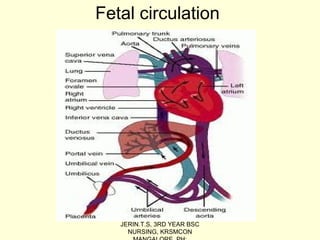
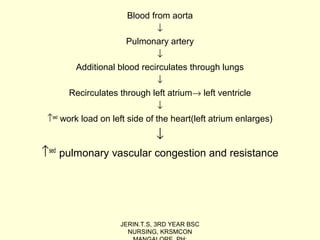
The document discusses the Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA), which is a persistent opening between the pulmonary artery and the aorta that usually closes shortly after birth. It provides details on the epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnostic measures, and management of PDA. PDA is more common in preterm infants and left untreated can cause complications like pulmonary hypertension, congestive heart failure, and infections. Treatment involves the use of medications like indomethacin or ibuprofen to close the opening or surgical ligation if medications fail. Nursing care focuses on relieving respiratory distress, improving cardiac output and oxygenation, adequate nutrition, and preventing infections.