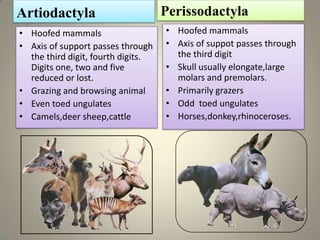
Mammals evolved from reptiles called Therapids during the Mesozoic era. They increased rapidly during the Cenozoic era. Mammals are characterized by having hair, mammary glands to feed young, and being warm-blooded. They are classified into monotremes, marsupials, and placentals. Placental mammals carry young to term in the uterus. There are 19 orders of mammals including rodents, bats, whales, carnivores, even-toed and odd-toed ungulates, primates, and more. Each order has distinct characteristics related to their evolution, habitats, diets and behaviors.