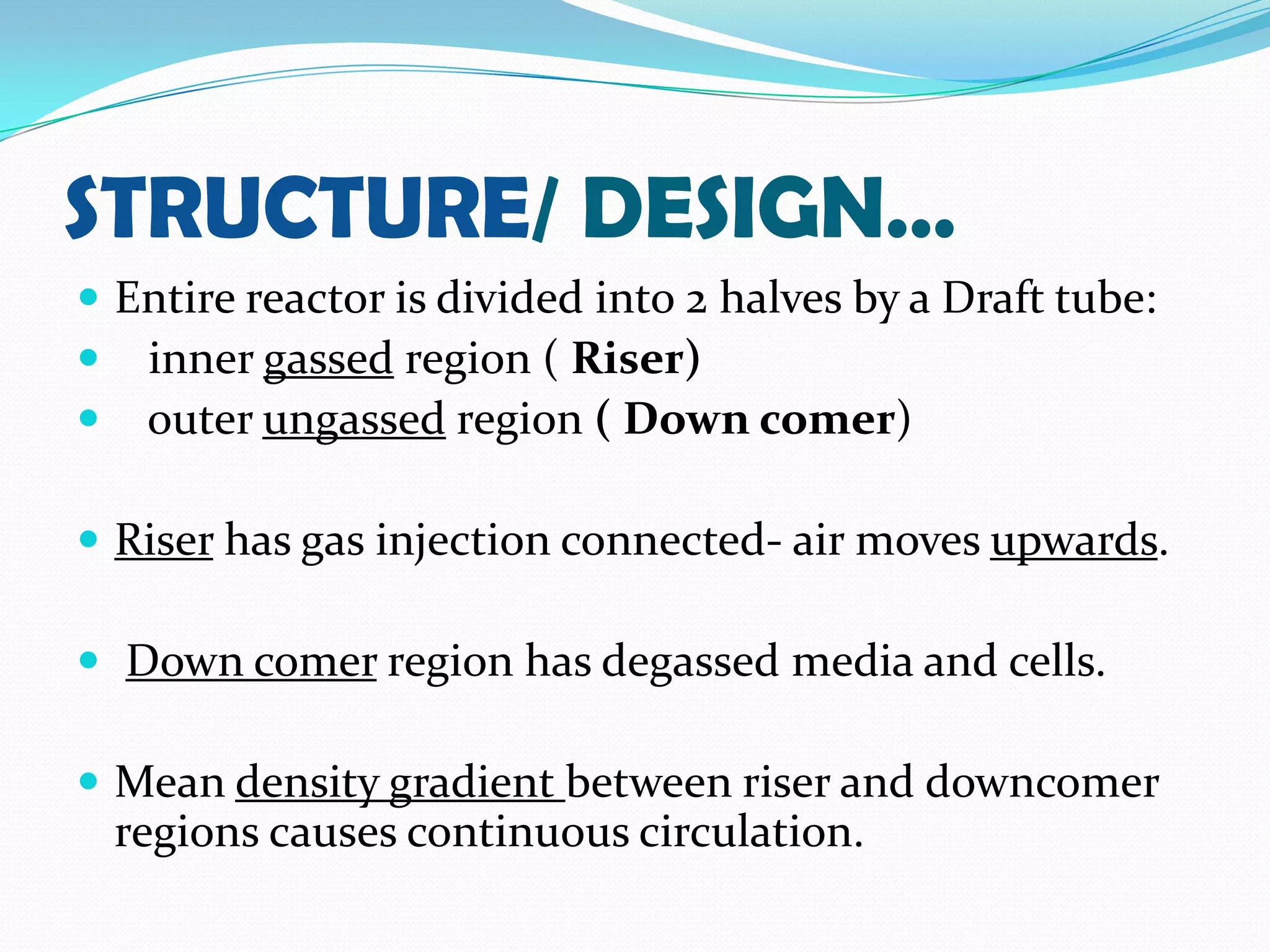
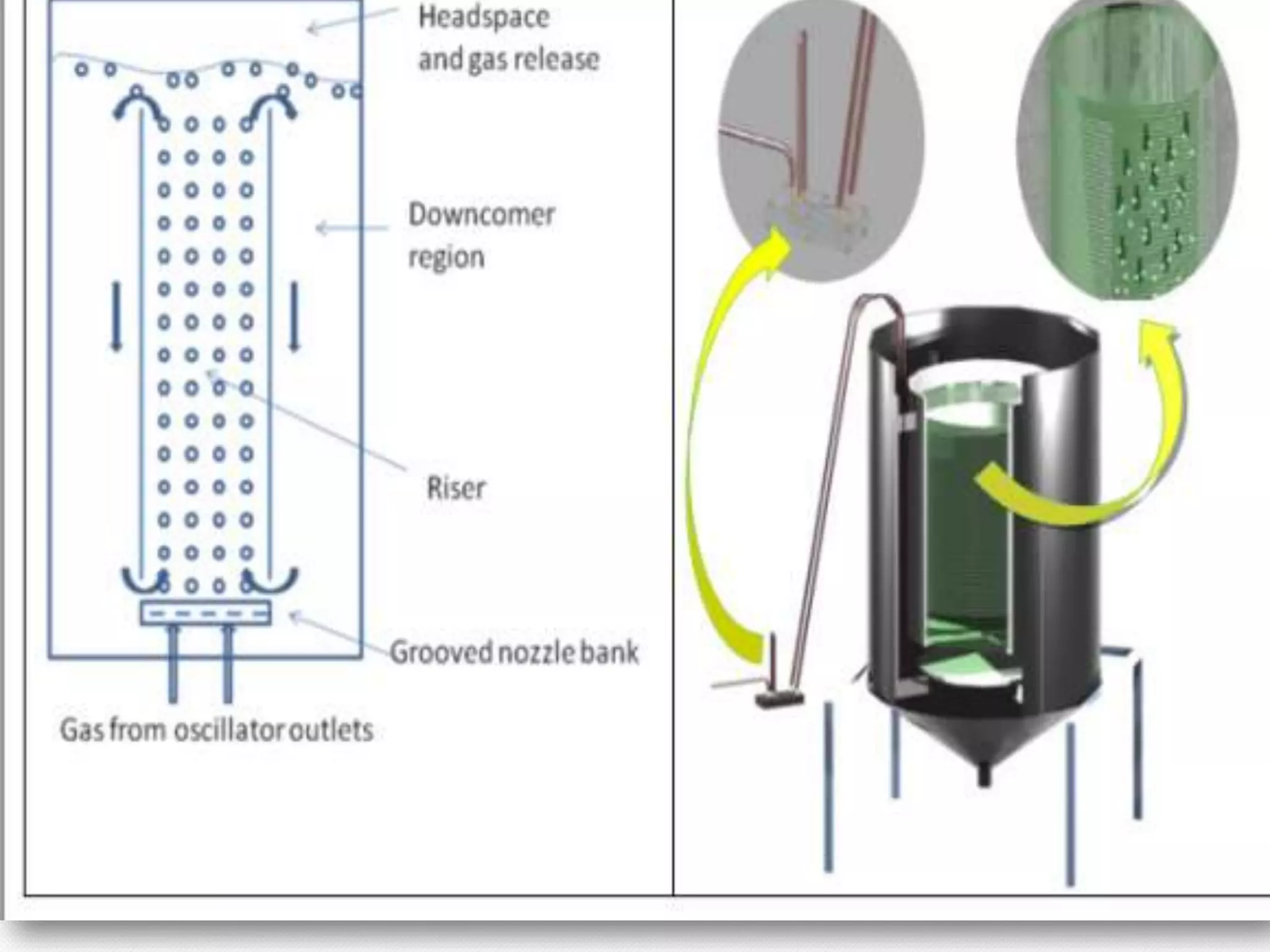
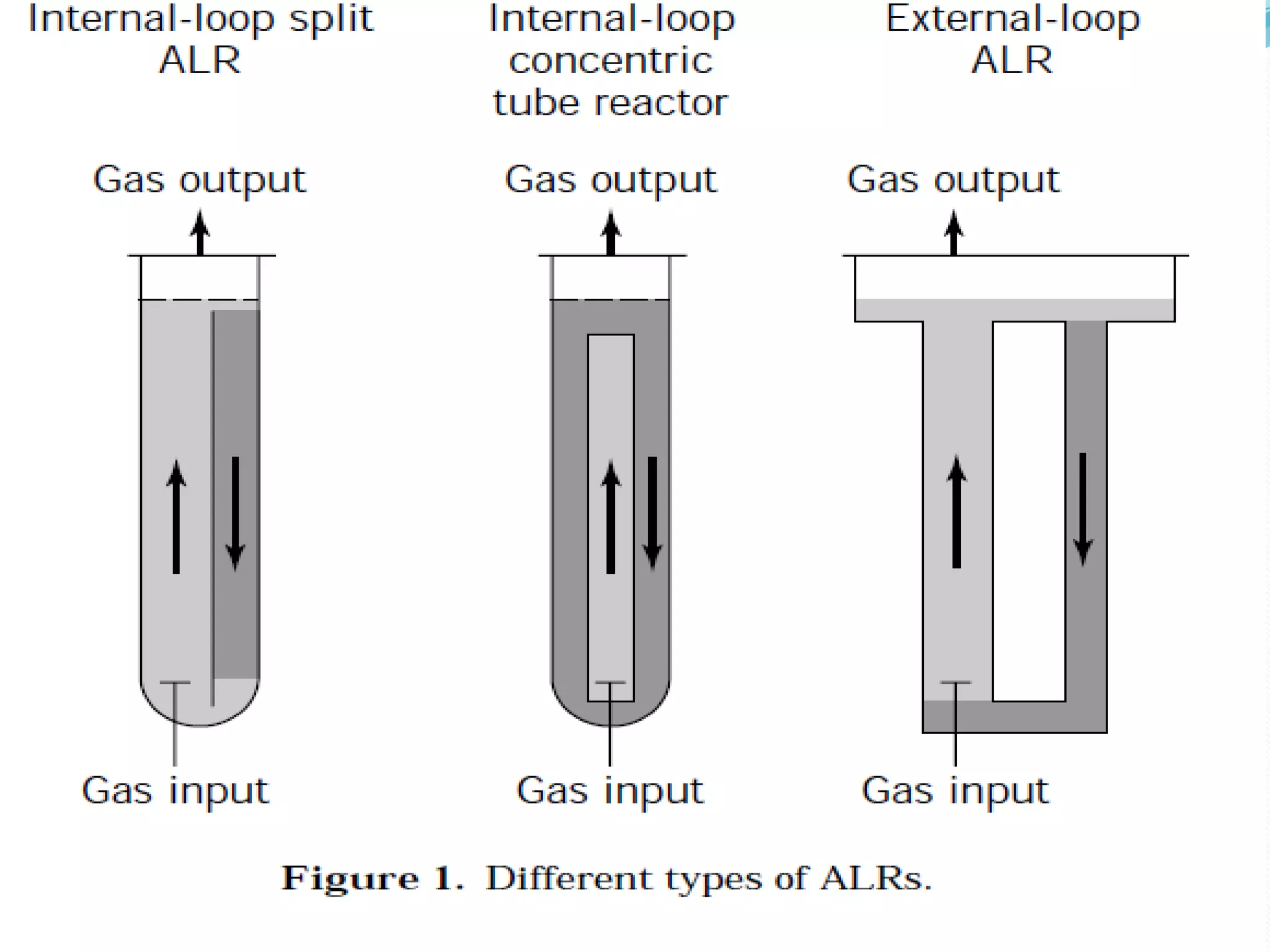
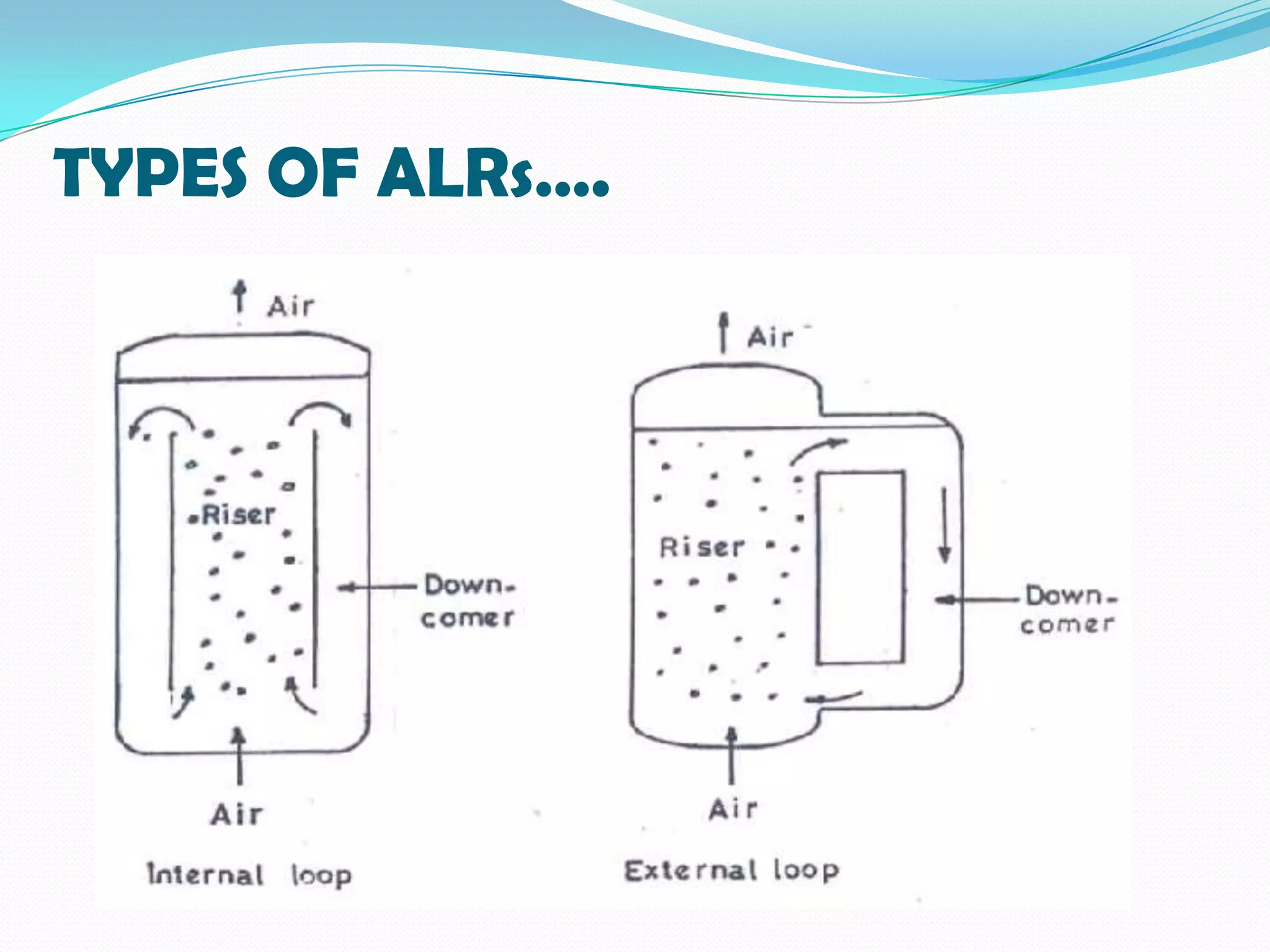
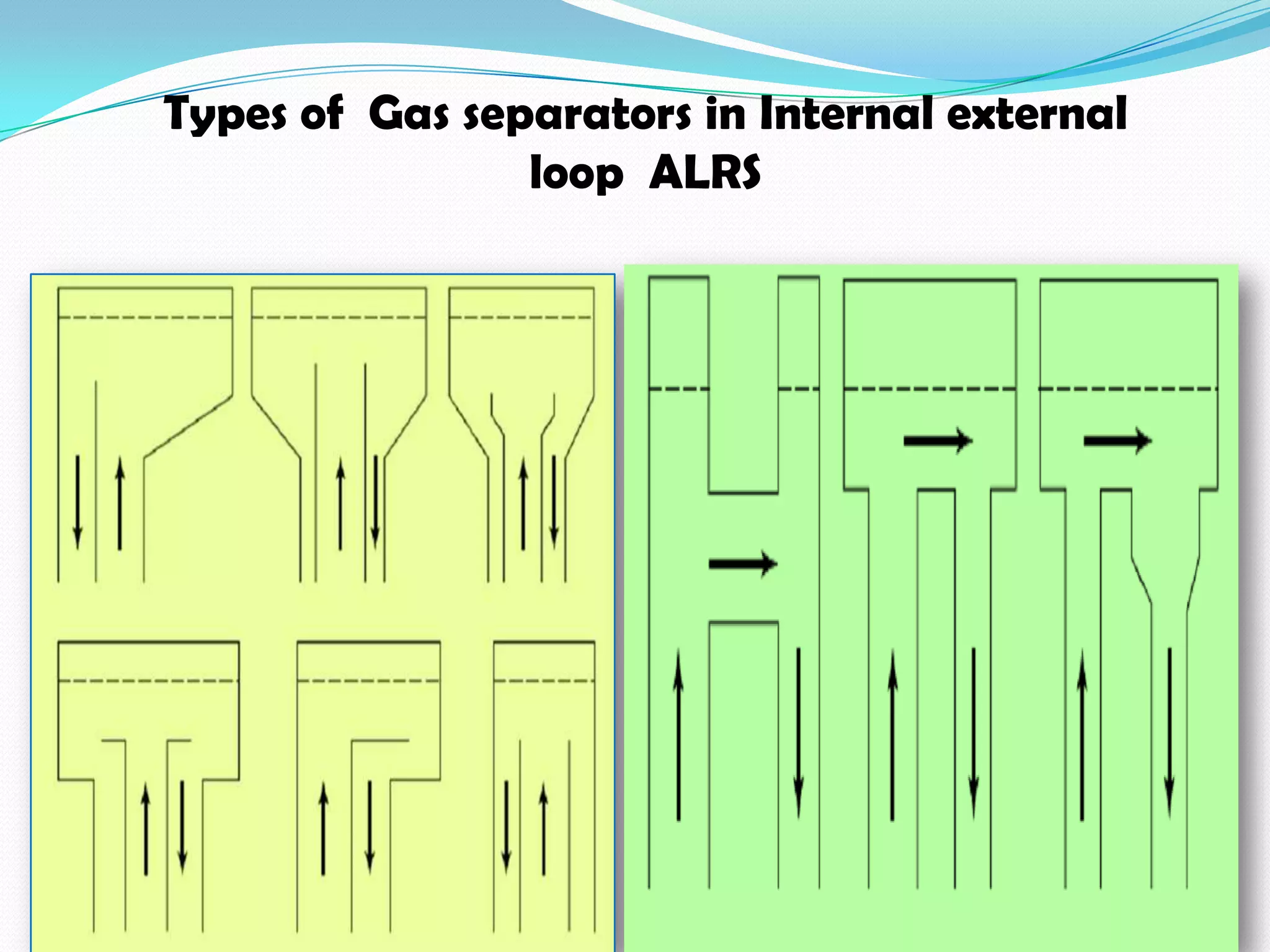
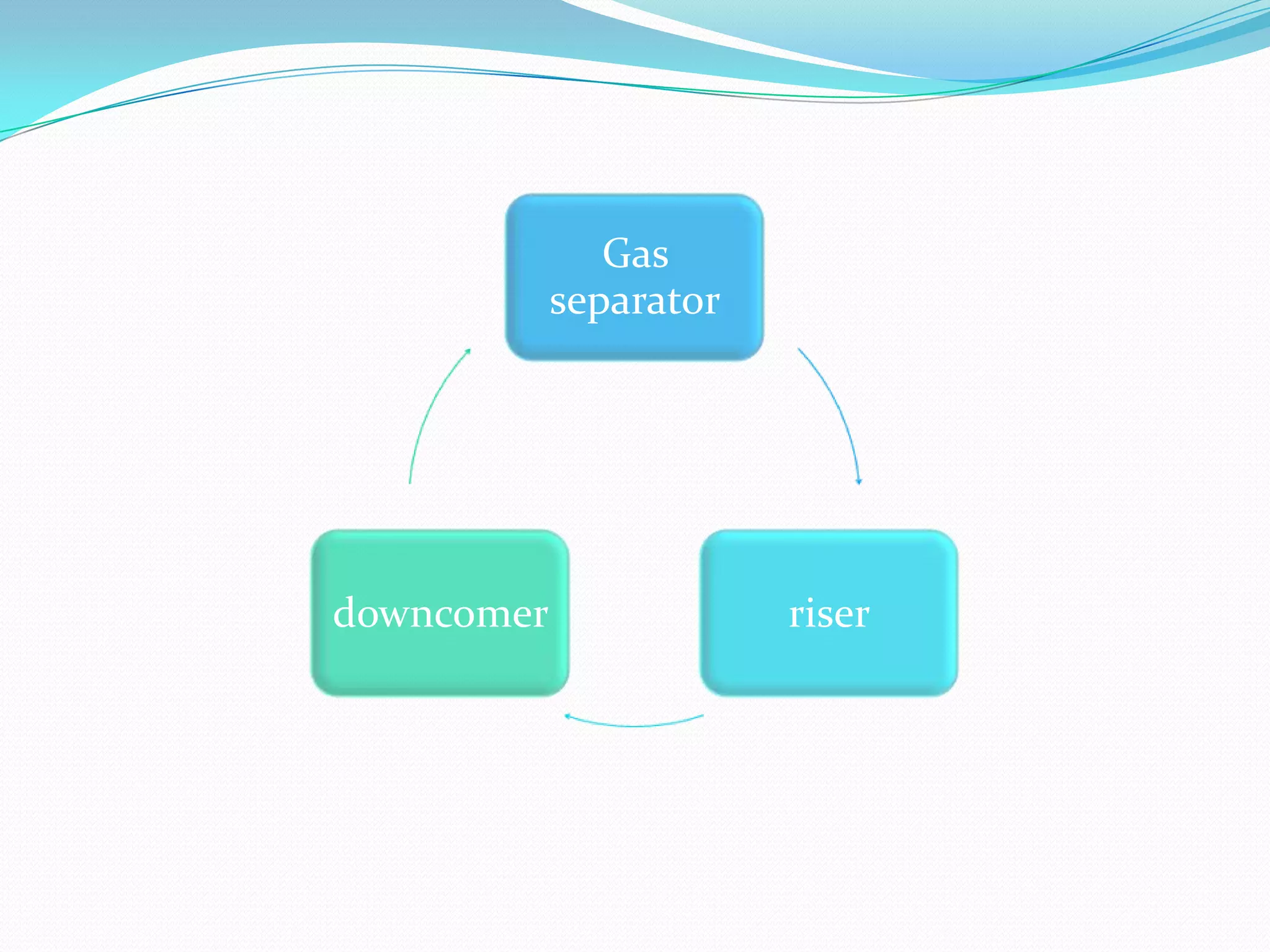
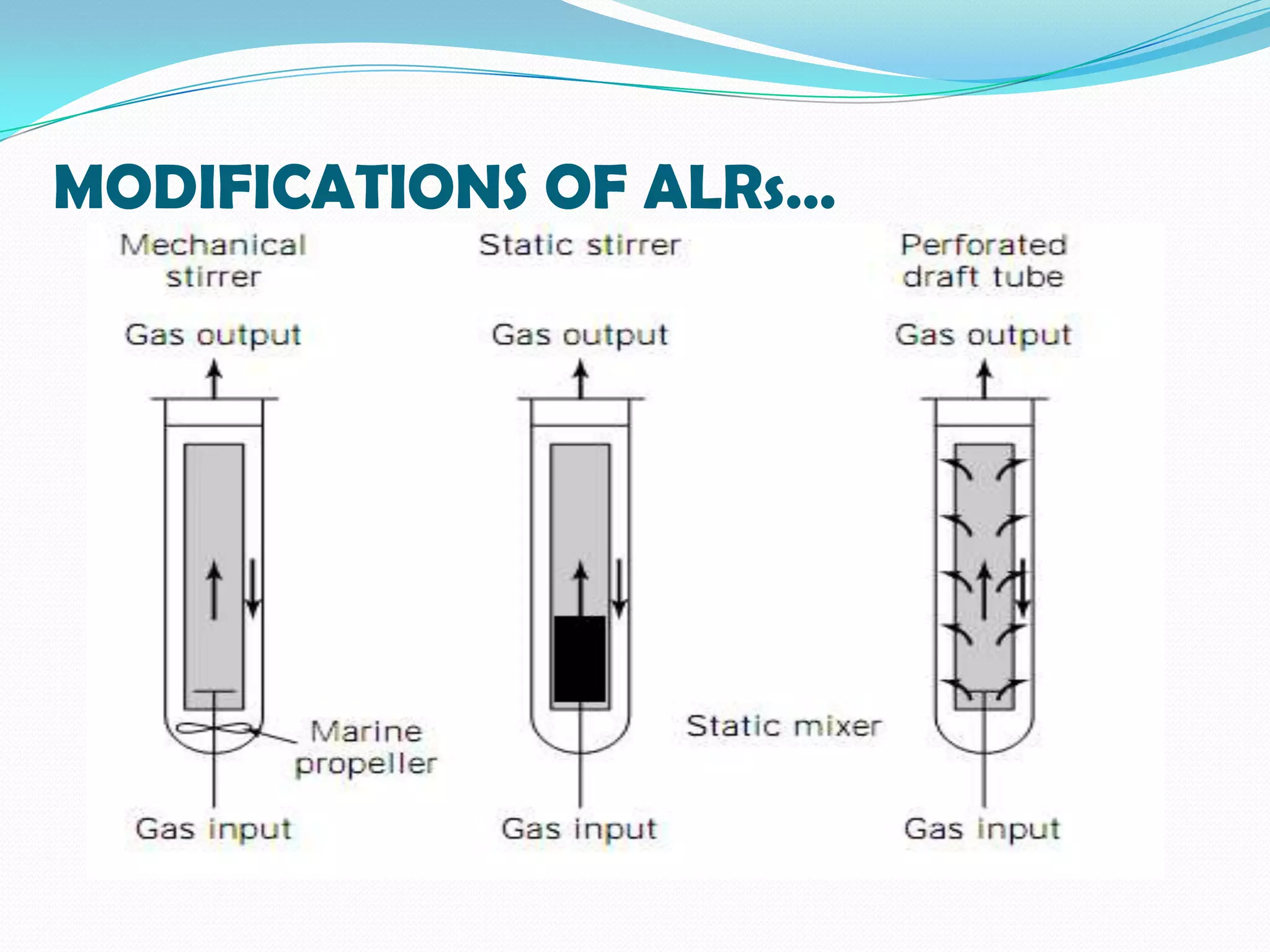
This document describes the airlift bioreactor, which uses forced air circulation to mix cells and nutrients without mechanical agitation. It has an inner riser region where air is injected upwards, and an outer downcomer region where degassed media and cells circulate downwards. The density gradient between these regions drives continuous fluid circulation. The bioreactor has a gas separator, sparger, and headspace to introduce air, separate gases, and allow foaming. It is useful for culturing shear-sensitive cells as it provides gentle mixing with low energy use.