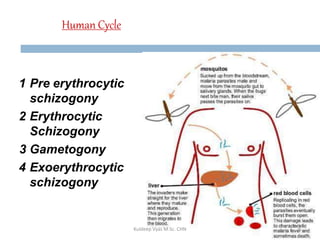
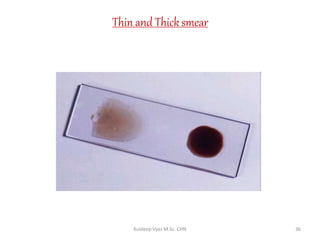
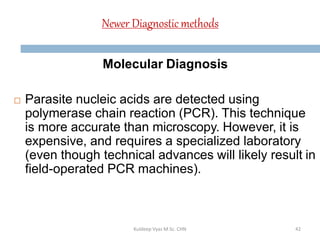
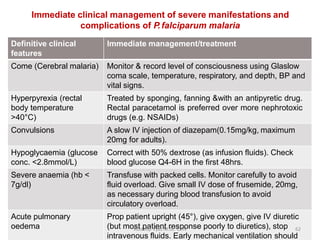
Malaria remains a critical global health issue, affecting over 40% of the world's population with approximately 350-500 million cases each year, including around 2 million cases and 1,000 deaths in India. The complex life cycle of the malaria parasite includes stages within both human hosts and mosquitoes, leading to various symptoms and clinical presentations, particularly with the severe complications associated with Plasmodium falciparum. Diagnosis typically involves blood examinations and can include advanced methods such as PCR, while treatment options range from traditional antimalarial drugs to newer therapies for severe cases.