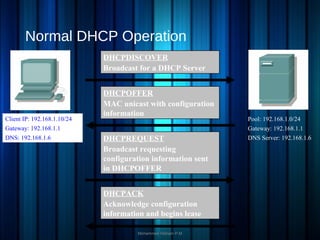
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a client/server protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses and configuration information to devices on a network, reducing the need for manual setup. It supports three methods of IP address allocation: dynamic, automatic, and static, with various message types for communication between clients and servers. While it offers benefits such as simplified management and mobility for users, DHCP relies on UDP, which is less secure and cannot utilize DNS for configured hosts.
![What is DHCP?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a client/server protocol that
automatically provides an Internet Protocol (IP) host with its IP address and other
related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway.
Clients should require no manual configuration by the user to connect to the
network.
Each client should be able to discover appropriate configuration information
dynamically.
This is normally accomplished through the use of a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol [UDP]
Mohammed Hisham P.M
DHCP
Requires little or no administrative overhead, after initial configurations of the
DHCP server.
Dynamically maps IP addresses to MAC addresses.
Addresses can be leased for a predefined amount of time before the lease
expires and must be renewed by the client.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acndhcp-161026172736/85/DHCP-Protocol-2-320.jpg)