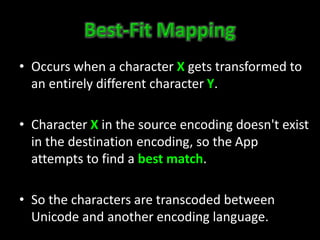
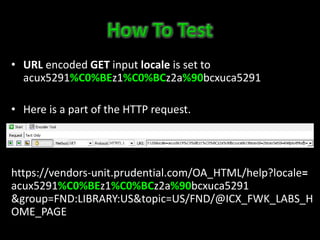
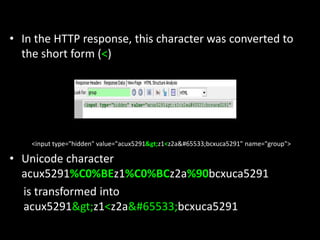
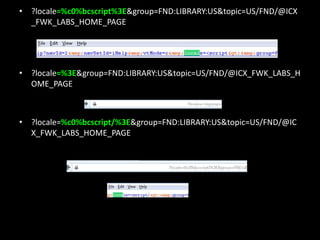
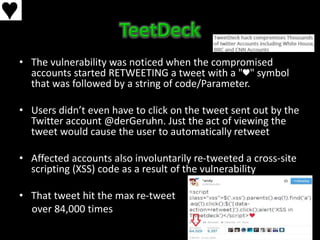
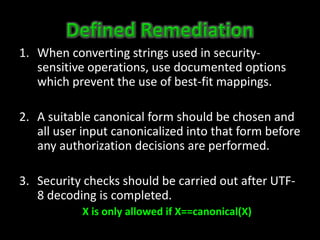
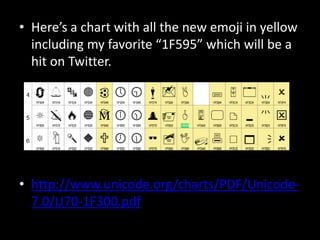
This document discusses Unicode transformation attacks and provides examples of how applications can be manipulated. It covers how Unicode lets systems support multiple languages, how characters are assigned unique numbers, and examples of lookalike characters. It also describes how data can be encoded to disguise malicious code, examples of bypassing filters by changing case or using lookalikes, and real world examples like compromising Spotify and Twitter accounts by creating usernames with special characters. The document recommends ways to prevent these issues, like canonicalizing input and performing security checks after decoding.