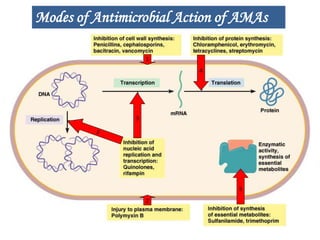
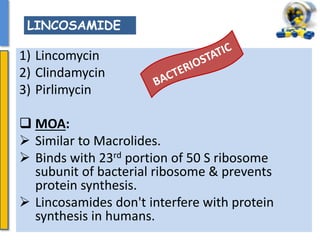
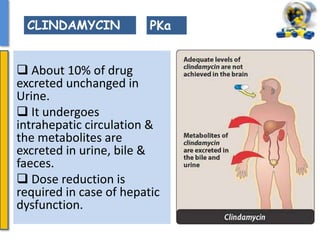
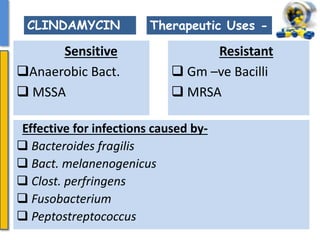
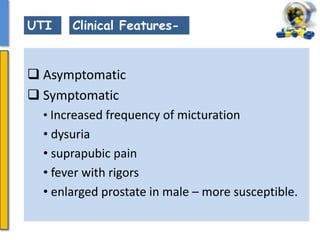
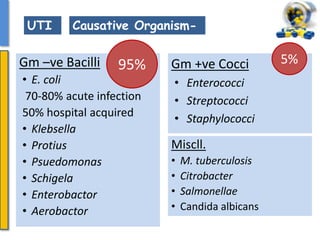
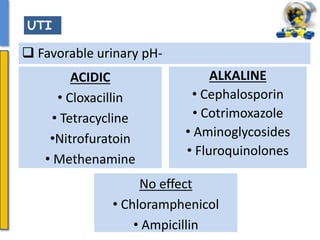
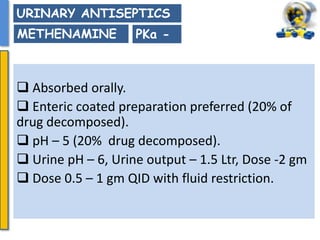
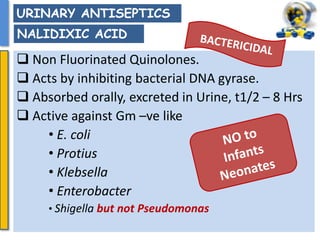
This document details the pharmacological aspects of lincosamides, glycopeptides, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). It covers the mechanisms of action, therapeutic uses, and resistance patterns of various antibiotics like clindamycin, vancomycin, and nitrofurantoin, along with the features and causative organisms of UTIs. Additionally, it discusses predisposing factors, clinical symptoms, and specific antibiotics effective in treating UTIs.