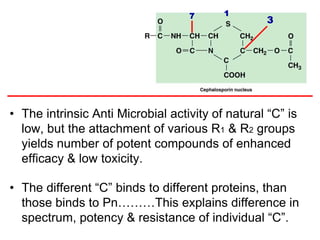
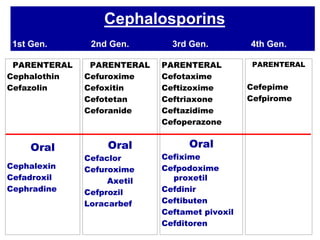
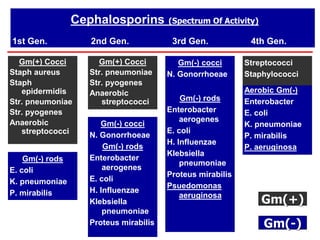
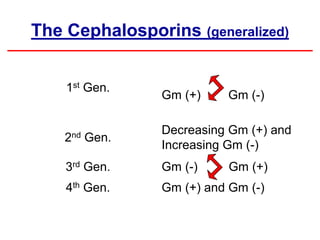
Cephalosporins are a class of antibiotics derived from the fungus Cephalosporium, with a structure comprising a dihydrothiazine and beta-lactam ring, acting primarily through a bactericidal mechanism similar to penicillins. They are categorized into four generations based on their antimicrobial activity, with varying effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and are primarily administered through parenteral routes due to poor oral absorption. While generally well tolerated, cephalosporins can exhibit allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disturbances, and specific adverse effects related to certain generations and side chains.