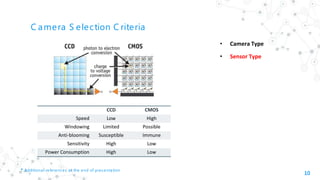
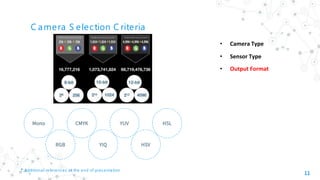
The document provides an overview of various types of industrial cameras, including line scan, area scan, 3D, thermal, network, and smart cameras, detailing their features, operational criteria, and applications. It also discusses camera selection criteria related to sensor type, output format, shutter type, and additional parameters necessary for effective operation in industrial environments. The document includes references for further reading on the technology and specifications of industrial cameras.

![What is an Industrial C amera?
[1 ]
◎ Imaging sensor packaged for industrial usage
◎ Improved performance, stability & reliability
◎ Easy installation & compact structure
◎ Long operational time
◎ High speed shutter time (order of micro-seconds)
◎ Higher frame rates (up to thousands of fps)
◎ Output raw data (uncompressed)
◎ Supports wide spectral range
2
http://pomeas.com/mobile/newsview/396.html [1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvcameras-200824064518/85/Machine-Vision-Cameras-2-320.jpg)