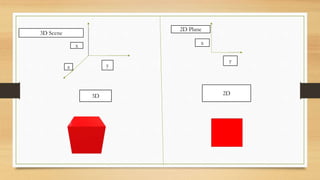
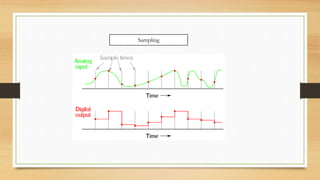
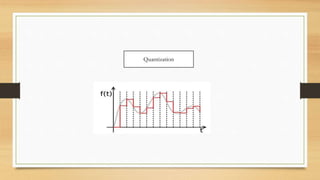
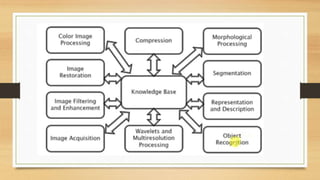
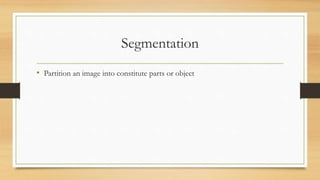
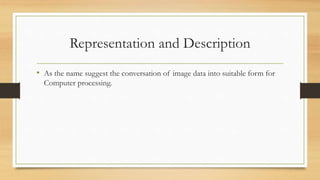
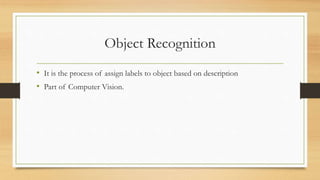
The document provides an overview of digital image processing, including definitions, types, advantages, and disadvantages of digital and analog images. It describes fundamental steps in image processing, applications such as image enhancement and recognition, and outlines methods for image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, and compression. The conclusion emphasizes the potential and future advancements in digital image processing as technology evolves.