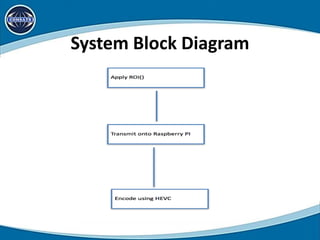
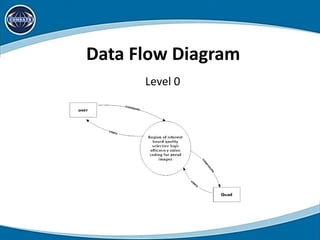
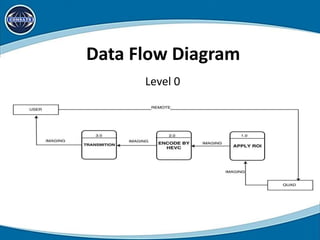
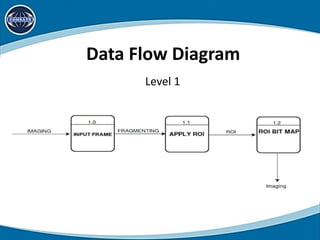
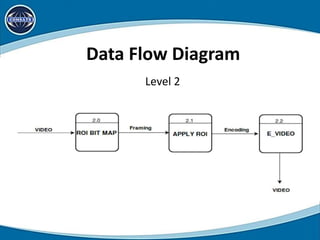
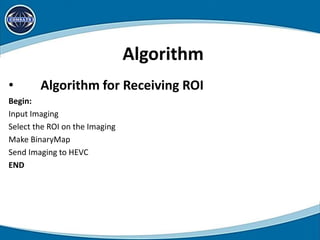
This document discusses using region of interest (ROI) with High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) to compress aerial videos. It proposes identifying ROIs in aerial images, applying HEVC encoding tailored to each ROI for better resolution and lower bandwidth usage, and transmitting the encoded video. The system would segment images, encode the tailored images using HEVC, and transmit them via FTP for viewing. It presents the scope, limitations, problem statement, tools and technologies used, system modules, use cases, data flow diagrams, algorithms, and conclusions of the proposed work. Future work could expand it to video conferencing by making faces the ROI.