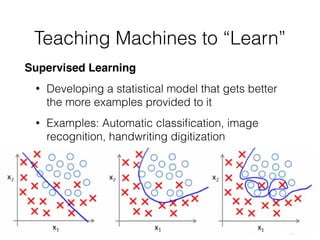
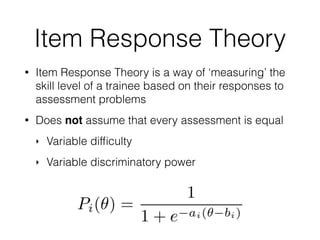
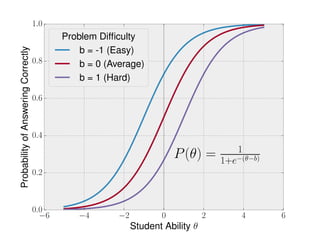
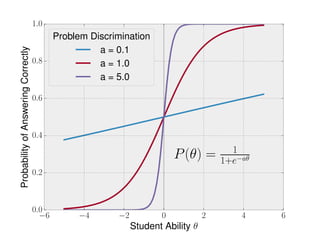
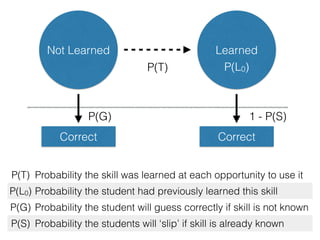
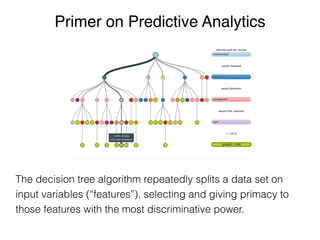
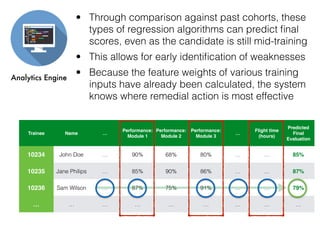
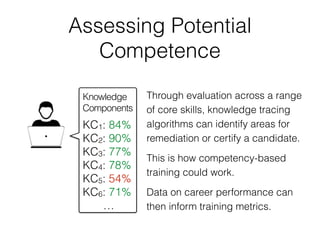
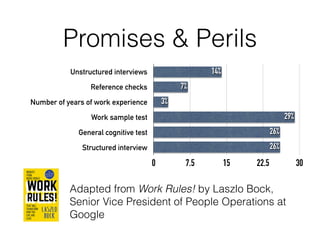
The document discusses the application of machine learning in aerospace training, emphasizing the use of big data and competency-based training approaches. It highlights techniques such as item response theory and Bayesian knowledge tracing for assessing trainee skills and predicting success using supervised learning models. The conclusion indicates that machine learning and AI are set to transform education and training in the industry towards more data-driven, adaptive methods.